Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Mechanisms > T - Z > Virtual Server
Virtual Server
The virtual server, also known as virtual machine (VM), is a form of virtualization software that emulates a physical server and is used by cloud providers to share the same physical server with multiple cloud consumers by providing cloud consumers with individual virtual server instances. Figure 1 shows three virtual servers being hosted by two physical servers. The number of instances a given physical server can share is limited by its capacity.
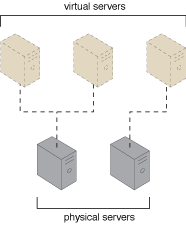
Figure 1 – The first physical server hosts two virtual servers, while the second physical server hosts one virtual server.
As a commodity mechanism, the virtual server represents the most foundational building block of cloud environments. Each virtual server can host numerous IT resources, cloud-based solutions, and various other cloud computing mechanisms. The instantiation of virtual servers from image files is a resource allocation process that can be completed rapidly and on-demand.
Cloud consumers that install or lease virtual servers can customize their environments independently from other cloud consumers that may be using virtual servers hosted by the same underlying physical server. Figure 2 depicts a virtual server that hosts a cloud service being accessed by Cloud Service Consumer B, while Cloud Service Consumer A accesses the virtual server directly to perform an administration task.
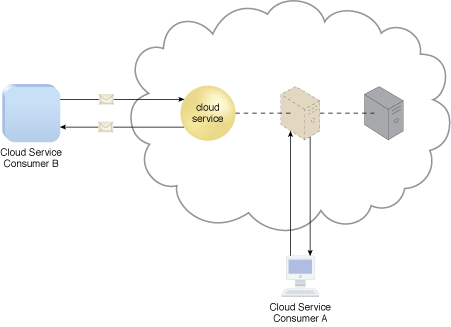
Figure 2 – A virtual server hosts an active cloud service and is further accessed by a cloud consumer for administrative purposes.
Related Patterns:
- Automated Administration
- Cloud VM Platform Encryption
- Direct I/O Access
- Direct LUN Access
- Dynamic Scalability
- Elastic Disk Provisioning
- Elastic Network Capacity
- Elastic Resource Capacity
- Hypervisor Clustering
- Hypervisor Clustering
- Leader Node Election
- Load Balanced Virtual Server Instances
- Load Balanced Virtual Switches
- Multipath Resource Access
- Non-Disruptive Service Relocation
- Persistent Virtual Network Configuration
- Persistent Virtual Network Configuration
- Platform Provisioning
- Rapid Provisioning
- Redundant Physical Connection for Virtual Servers
- Resource Pooling
- Resource Reservation
- Service State Management
- Shared Resources
- Single Node Multi-Containers
- Synchronized Operating State
- Workload Distribution
- Zero Downtime
- Zero Downtime
This mechanism is covered in CCP Module 2: Cloud Technology Concepts.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is covered in:
Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture by Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood,
Ricardo Puttini
(ISBN: 9780133387520, Hardcover, 260+ Illustrations, 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

