Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Data Management and Storage Device Patterns > RAID-Based Data Placement
RAID-Based Data Placement (Cope, Erl)
How can data be stored on a RAID level that matches its required performance and protection levels?

Problem
Cloud storage devices can be provisioned with different underlying and back-end RAID levels. Data placed on a RAID level that is incompatible with its performance or protection requirements can be in jeopardy of underperforming or failing.
Solution
An interface is provided to cloud consumers that can communicate information about the available underlying RAID levels of cloud storage devices.
Application
A RAID identifier mechanism is used to inform the cloud consumer of RAID levels available for a selected cloud storage device by directly interacting with the cloud storage management portal mechanism.
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
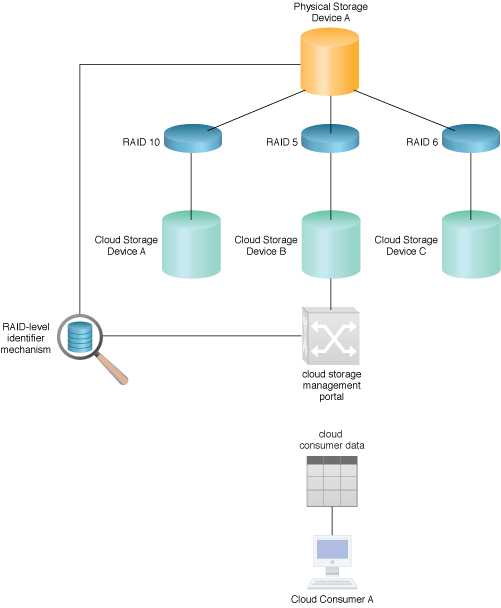
A RAID-level identifier mechanism will use the cloud storage management portal mechanism to return information on the specifics of the cloud storage devices to Cloud Consumer A.
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 14: Advanced Cloud Storage.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
The architectural model upon which this design pattern is based is further covered in:
Cloud Computing Design Patterns by Thomas Erl, Robert Cope, Amin Naserpour
(ISBN: 9780133858563, Hardcover, ~ 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

