SOA Patterns > Service Messaging Patterns > Intermediate Routing
Intermediate Routing (Little, Rischbeck, Simon)
How can dynamic runtime factors affect the path of a message?

Problem
The larger and more complex a service composition is, the more difficult it is to anticipate and design for all possible runtime scenarios in advance, especially with asynchronous, messagingbased communication.
Solution
Message paths can be dynamically determined through the use of intermediary routing logic.
Application
Various types of intermediary routing logic can be incorporated to create message paths based on message content or runtime factors.
Impacts
Dynamically determining a message path adds layers of processing logic and correspondingly can increase performance overhead. Also the use of multiple routing logic can result in overly complex service activities.
Architecture
Composition
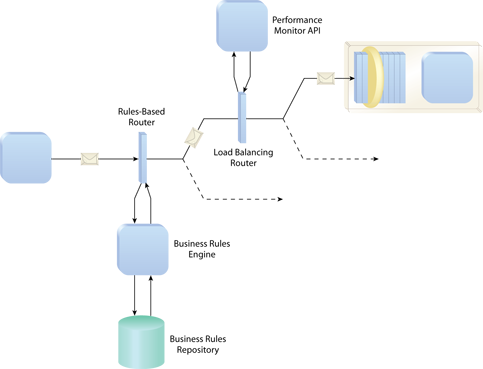
A message passes through two router agents before it arrives at its destination. The Rules-Based Router identifies the target service based on a business rule that the agent dynamically retrieves and interprets, as a consequence of Rules Centralization. The Load Balancing Router then checks current usage statistics for that service before it decides which instance or redundant implementation of the service to send the message to.
Related Patterns in This Catalog
Canonical Resources, Event-Driven Messaging, Messaging Metadata, Service Agent, Service Messaging
Related Patterns in Other Catalogs
Content-Based Router, Dynamic Router, Message Router
Related Service-Oriented Computing Goals
This pattern is covered in SOACP Module 7: Advanced SOA Design & Architecture with Services & Microservices.
For more information regarding the SOA Certified Pofessional (SOACP) curriculum,
visit www.arcitura.com/soa.
This page contains excerpts from:
SOA Design Patterns by Thomas Erl
(ISBN: 0136135161, Hardcover, Full-Color, 400+ Illustrations, 865 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

