Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Mechanisms > I - P > Pay-Per-Use Monitor
Pay-Per-Use Monitor

The pay-per-use monitor mechanism measures cloud-based IT resource usage in accordance with predefined pricing parameters and generates usage logs for fee calculations and billing purposes.
Some typical monitoring variables are:
- request/response message quantity
- transmitted data volume
- bandwidth consumption
The data collected by the pay-per-use monitor is processed by a billing management system that calculates the payment fees.
Figure 1 shows a pay-per-use monitor implemented as a resource agent used to determine the usage period of a virtual server.
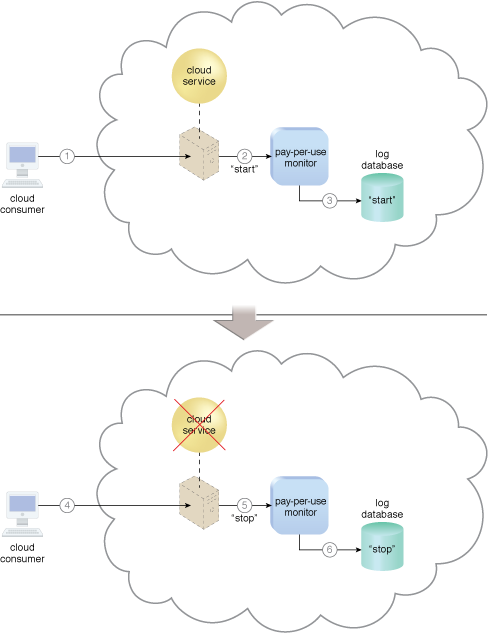
Figure 1 – A cloud consumer requests the creation of a new instance of a cloud service (1). The IT resource is instantiated and they pay-per-use monitor mechanism receives a “start” event notification from the resource software (2). The pay-per-use monitor stores the value timestamp in the log database (3). The cloud consumer later requests that the cloud service instance be stopped (4). The pay-per-use monitor receives a “stop” event notification from the resource software (5) and stores the value timestamp in the log database (6).
Figure 1 illustrates the pay-per-use monitor designed as a monitoring agent that transparently intercepts and analyzes runtime communication with a cloud service.
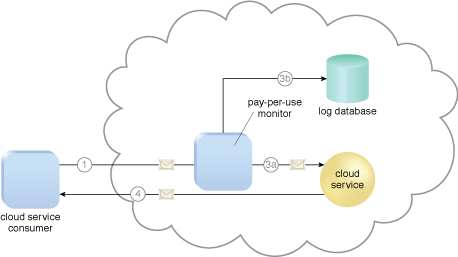
Figure 2 – A cloud service consumer sends a request message to the cloud service (1). The pay-per-use monitor intercepts the message (2), forwards it to the cloud service (3a), and stores the usage information in accordance with its monitoring metrics (3b). The cloud service forwards the response messages back to the cloud service consumer to provide the requested service (4).
Related Patterns:
- Centralized Remote Administration
- Cross-Storage Device Vertical Tiering
- Direct I/O Access
- Direct LUN Access
- Dynamic Scalability
- Elastic Disk Provisioning
- Elastic Network Capacity
- Elastic Resource Capacity
- Intra-Storage Device Vertical Data Tiering
- Non-Disruptive Service Relocation
- Pay-as-You-Go
- Resource Pooling
- Rich Container
- Service State Management
- Usage Monitoring
This mechanism is covered in CCP Module 2: Cloud Technology Concepts.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is covered in:
Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture by Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood,
Ricardo Puttini
(ISBN: 9780133387520, Hardcover, 260+ Illustrations, 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

