Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Reliability, Resiliency and Recovery Patterns > Multipath Resource Access
Multipath Resource Access (Erl, Naserpour)
How can an IT resource be accessed when its pre-defined path is lost or becomes unavailable?

Problem
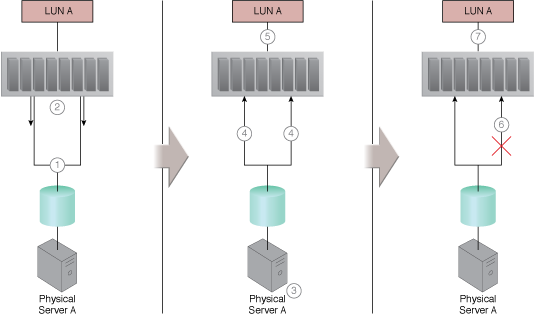
When the path to an IT resource is lost or becomes unavailable, the IT resource becomes inaccessible. This can jeopardize the stability of an entire cloud-based solution until the cloud provider is able to supply the cloud consumer with the lost or updated path.
Solution
Alternative paths to IT resources are provided to give cloud consumers a means of programmatically or manually overcoming path failures.
Application
A multipathing system that resides on the server or hypervisor is established to provide multiple alternative paths to the same, unique IT resource, while ensuring that the IT resource is viewed identically via each alternative path.
Mechanisms
Cloud Storage Device, Hypervisor, Logical Network Perimeter, Resource Replication, Virtual Server
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
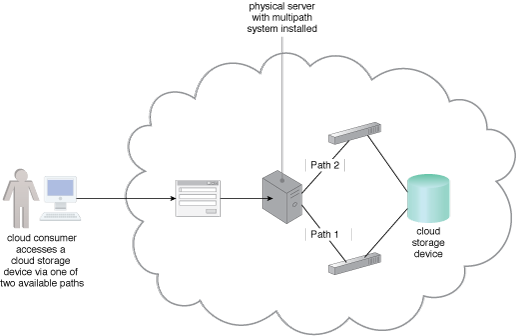
A multipathing system providing alternative paths to a cloud storage device.
An example of a multipathing system.
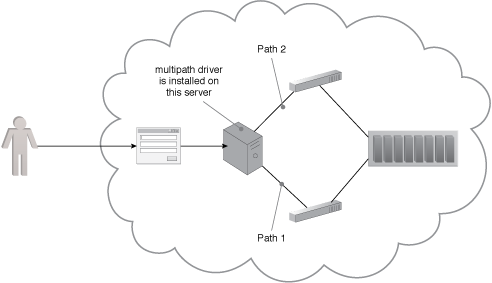
A multipath driver is installed on a server to ensure that the operating system understands the redundant paths and views two paths leading to the same IT resource as two separate IT resources.
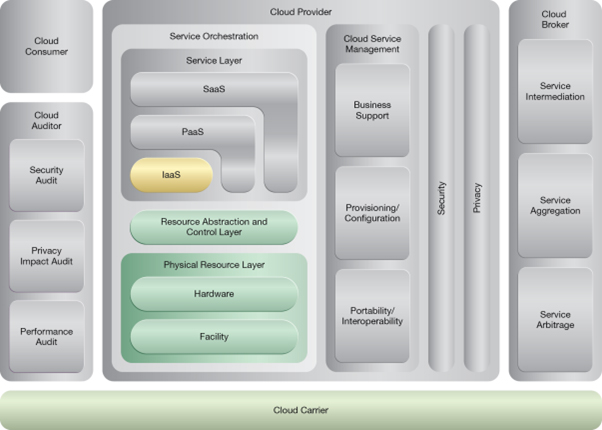
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 4: Fundamental Cloud Architecture.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 14: Advanced Cloud Storage.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is covered in:
Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture by Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood,
Ricardo Puttini
(ISBN: 9780133387520, Hardcover, 260+ Illustrations, 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


