Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Virtual Server and Hypervisor Connectivity and Management Patterns > Virtual Server-to-Virtual Server Anti-Affinity
Virtual Server-to-Virtual Server Anti-Affinity (Erl, Naserpour)
How can virtual servers and bundled workloads be guaranteed to not be hosted by the same hypervisor?
Problem
Certain virtual servers or bundled workloads need to be hosted on different hosts.
Solution
Anti-affinity rules are used to ensure that the virtual servers or bundled workload are never simultaneously hosted together by the same destination host.
Application
Affinity rules are applied and configured by the application of the Virtual Server-to-Virtual Server Anti-Affinity pattern, and are controlled and dedicated by the VIM server.
Mechanisms
Hypervisor, Live VM Migration, Virtual Infrastructure Manager
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
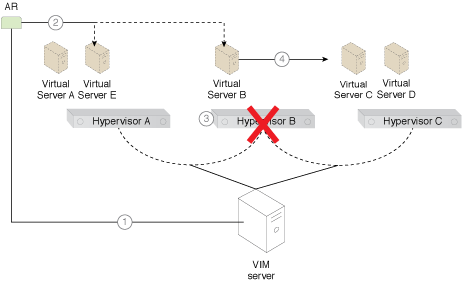
The steps comprising the application of the pattern are illustrated (Part I).
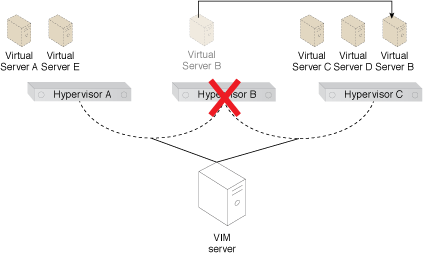
Virtual Server B is moved to Hypervisor C, after the system learns of the anti-affinity rule defined for Virtual Servers A and B (Part II).
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 17: Advanced Cloud Virtualization.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
