Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Data Management and Storage Device Patterns > Cloud Storage Data Lifecycle Management
Cloud Storage Data Lifecycle Management (Cope, Erl)
How can data be stored and managed in a cloud environment based on a defined lifecycle?
Problem
Datasets no longer required by an organization can bloat databases causing performance challenges, and can further incur administration and maintenance burdens.
Solution
A solution can be introduced to automatically manage and migrate the data into a different type of cloud storage device, or delete the data based on its state in a defined lifecycle.
Application
A cloud storage data aging management mechanism monitors the state of data against a provided lifecycle in order to move data to a different cloud storage device or delete data after a defined lifecycle.
Mechanisms
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
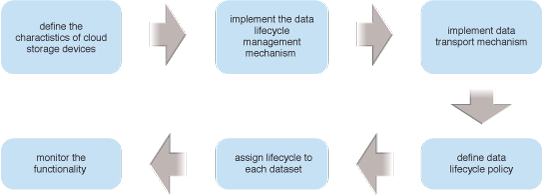
The steps in applying the Cloud Storage Data Lifecycle Management pattern are illustrated.
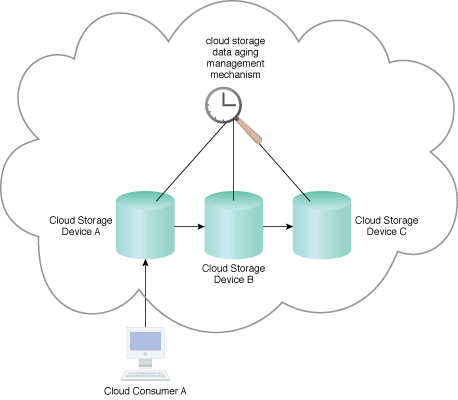
The cloud storage data aging management mechanism can be used in applying this pattern to manage datasets based on predefined policies.
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 14: Advanced Cloud Storage.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
The architectural model upon which this design pattern is based is further covered in:
Cloud Computing Design Patterns by Thomas Erl, Robert Cope, Amin Naserpour
(ISBN: 9780133858563, Hardcover, ~ 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

