Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Network Security, Identity & Access Management and Trust Assurance Patterns > Trust Attestation Service
Trust Attestation Service (Cope, Erl)
How can the security status of a cloud platform be communicated to cloud consumers?

Problem
Cloud platform security can be opaque to the cloud consumer that has compliance and regulatory security requirements. This can compromise the ability to verify the platform assurance level, which may be critical for some federal and regulated organizations.
Solution
An attestation service is implemented to maintain a trust policy for every attested host and to evaluate reports from the hardware roots of trust from trusted platform modules (TPMs) on each node to determine whether each node has undergone a trusted boot and is in compliance with the security policy.
Application
An attestation service provides assurance that the protected environment is correctly invoked using the TPM, measuring the integrity by validating digital signatures on the software running in the protected environment. An attestation identity key credential exchanged during a secure boot is used to establish mutual trust between the TPM and the attestation service. The orchestration engine uses the attestation service to select the appropriate compute platform required by workloads.
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
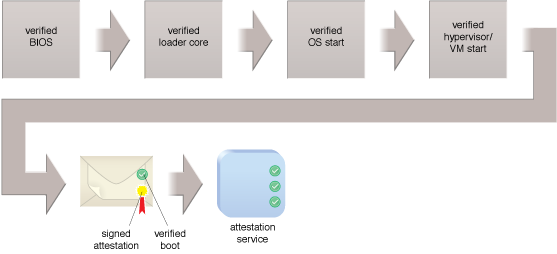
A trusted platform boot process.
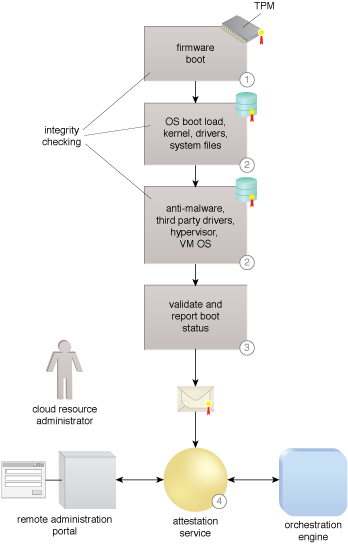
A secure boot with trust attestation.
This mechanism is covered in CCP Module 7: Fundamental Cloud Security and
in Module 8: Advanced Cloud Security.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
The architectural model upon which this design pattern is based is further covered in:
Cloud Computing Design Patterns by Thomas Erl, Robert Cope, Amin Naserpour
(ISBN: 9780133858563, Hardcover, ~ 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


