Microservice and Containerization Patterns > Containerization Patterns > Micro Scatter-Gather
Micro Scatter-Gather (Erl, Naserpour)
How can a microservice carry out high-performance composition logic that can include composing specific microservice instances?

Problem
Solution
Application
A container is established and assigned the role of root container for the distributed composition system. The root container hosts distributor and aggregator microservices. The distributor is responsible for breaking down a greater task into granular tasks and distributing those tasks to other microservices or microservice instances. The aggregator is responsible for aggregating the results from the composed microservices or microservice instances.
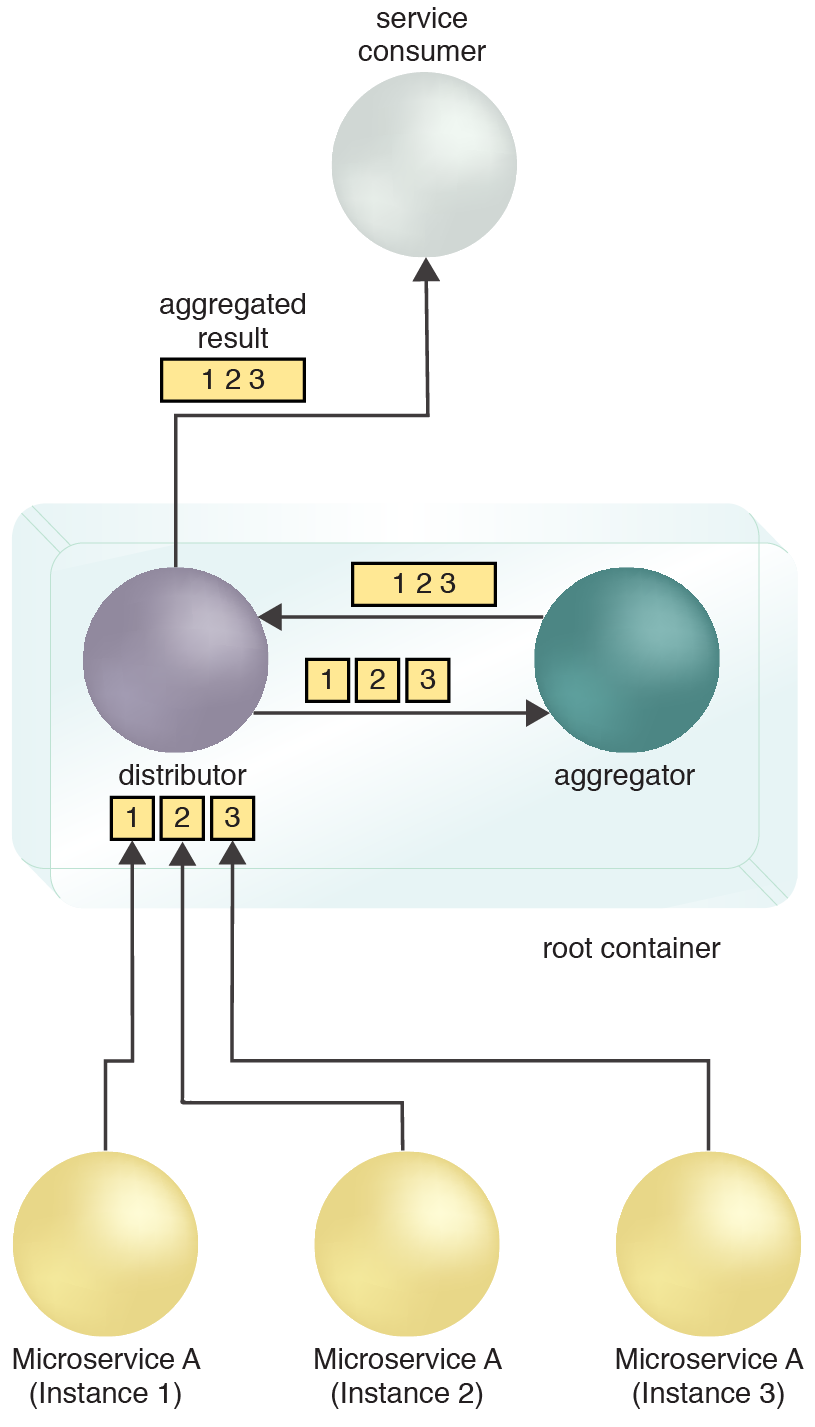
The microservice instances send their task results to the root container and its distributor service. The distributor forwards the results to the aggregator. The aggregator sends back the aggregated result to the distributor and the distributor returns the aggregated results to the service consumer.
This pattern can be applied by determining the number of instances of the root container that may be required, as explained in the complete pattern description.
This pattern is covered in Module 10: Advanced Microservice Architecture & Containerization..
For more information regarding microservice and containerization courses and accreditation,
visit the Microservice Architect Certification program page..
