Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Basics > Cloud Delivery Models > Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
A software program positioned as a shared cloud service and made available as a “product” or generic utility represents the typical profile of a SaaS offering. The SaaS delivery model is typically used to make a reusable cloud service widely available (often commercially) to a range of cloud consumers. An entire marketplace exists around SaaS products that can be leased and used for different purposes and via different terms (Figure 1).
A cloud consumer is generally granted very limited administrative control over a SaaS implementation. It is most often provisioned by the cloud provider, but it can be legally owned by whichever entity assumes the cloud service owner role. For example, an organization acting as a cloud consumer while using and working with a PaaS environment can build a cloud service that it decides to deploy in that same environment as a SaaS offering. The same organization then effectively assumes the cloud provider role as the SaaS-based cloud service is made available to other organizations that act as cloud consumers when using that cloud service.
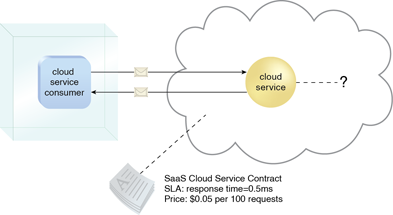
Figure 1 – The cloud service consumer is given access the cloud service contract, but not to any underlying IT resources or implementation details.

