Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Mechanisms > I - P > Malware Hash
Malware Hash

Hashing is a process that transforms arbitrary-length data into a small, fixed-length string of characters called a digest or message digest. Malware hashes are used by virus protection systems to identify viruses. They consist of calculated numerical values of code unique to the virus. Anti-virus software compares hashes of malware with hashes of software components within a computer system to detect malware.
Figure 1 shows the creation of a malware hash by generating a cryptographic hash of the malware code to create a digest that can be used by anti-virus software to identify a virus. Malware authors have learned to customize viruses for each infected machine, creating unique hashes for each copy delivered that challenge anti-virus systems.
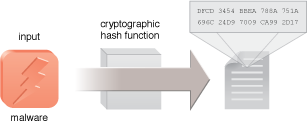
Figure 1 – An example of the creation of a hash of malware code.
Related Patterns:
This mechanism is covered in CCP Module 7: Fundamental Cloud Security and
in Module 8: Advanced Cloud Security.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
The architectural model upon which this design pattern is based is further covered in:
Cloud Computing Design Patterns by Thomas Erl, Robert Cope, Amin Naserpour
(ISBN: 9780133858563, Hardcover, ~ 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


