Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Mechanisms > I - P > Live VM Migration
Live VM Migration
Also referred to as live migration, the live VM migration mechanism is a system that is capable of relocating virtual servers or virtual server instances at runtime.
The example in Figures 1 and 2 demonstrate live VM migration as follows:
A virtual server capable of auto-scaling experiences an increase in its workload.
The VIM decides that the virtual server cannot scale up because its underlying physical server host is being used by other virtual servers.
The VIM commands the hypervisor on the busy physical server to suspend execution of the virtual server.
The VIM then commands the instantiation of the virtual server on the idle physical server.
State information (such as dirty memory pages and processor registers) is synchronized.
The VIM commands the hypervisor at the new physical server to resume the virtual server processing.
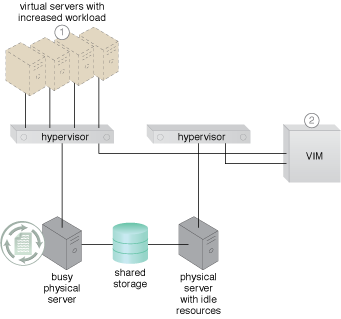
Figure 1 – An example demonstrating live VM migration (Part I).
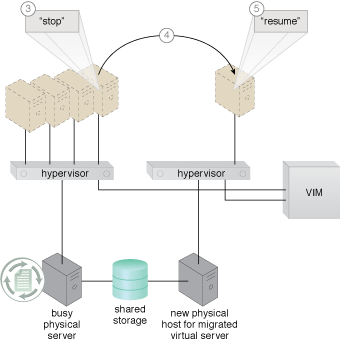
Figure 2 – An example demonstrating live VM migration (Part II).
Related Patterns:
- Cross-Hypervisor Workload Mobility
- Elastic Resource Capacity
- Load Balanced Virtual Server Instances
- Non-Disruptive Service Relocation
- Power Consumption Reduction
- Secure Connection for Scaled VMs
- Virtual Server-to-Host Affinity
- Virtual Server-to-Host Anti-Affinity
- Virtual Server-to-Virtual Server Affinity
- Virtual Server-to-Virtual Server Anti-Affinity
- Zero Downtime
This mechanism is covered in CCP Module 7: Fundamental Cloud Security and
in Module 8: Advanced Cloud Security.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
The architectural model upon which this design pattern is based is further covered in:
Cloud Computing Design Patterns by Thomas Erl, Robert Cope, Amin Naserpour
(ISBN: 9780133858563, Hardcover, ~ 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


