Microservice and Containerization Patterns > Scalability Patterns > Workload Distribution
Workload Distribution (Erl, Naserpour)
How can microservice over-utilization be avoided?

Problem
Solution
Application
The microservice is horizontally scaled via the addition of one or more identical microservices and a load balancing system further extends the deployment architecture to provide runtime logic capable of evenly distributing the workload across.
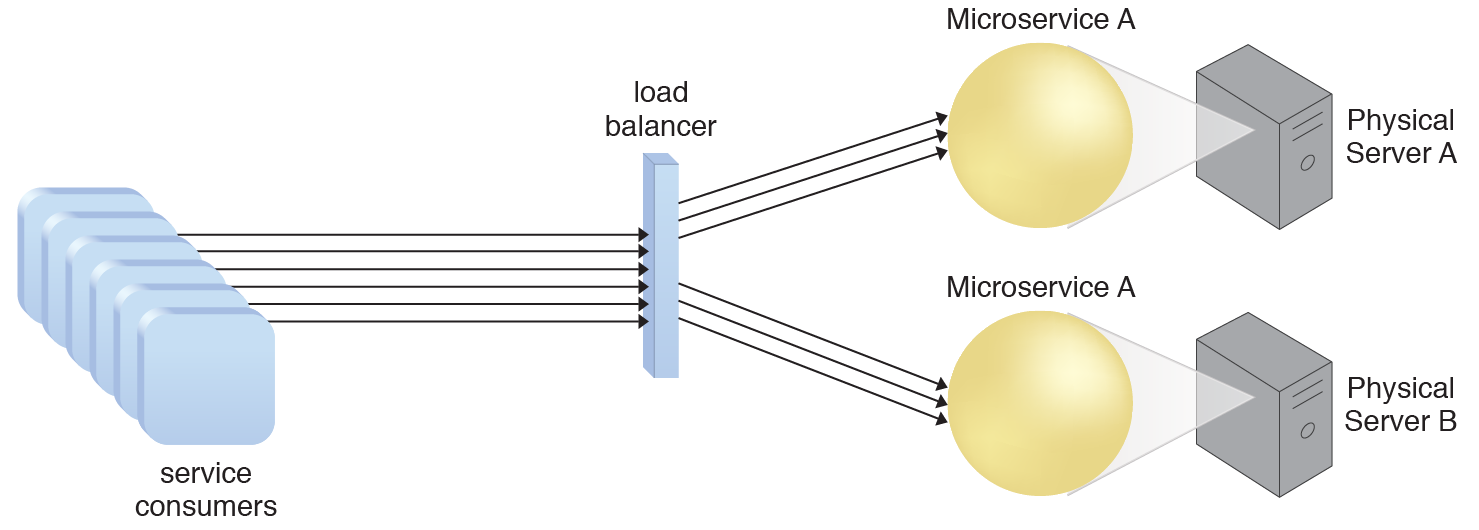
A redundant copy of Microservice A is implemented on Physical Server B. The load balancer intercepts the service consumer requests and directs them to both Physical Server A and B to ensure even distribution of the workload.
This pattern can be applied via the use of a load balancer, as explained in the complete pattern description.
This pattern is covered in Module 10: Advanced Microservice Architecture & Containerization..
For more information regarding microservice and containerization courses and accreditation,
visit the Microservice Architect Certification program page..
