Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Basics > Cloud Deployment Models > Private Clouds
Private Clouds
A private cloud is owned by a single organization. Private clouds enable an organization to use cloud computing technology as a means of centralizing access to IT resources by different parts, locations, or departments of the organization. When a private cloud exists as a controlled environment, the problems described in the Risks and Challenges section do not tend to apply.
The use of a private cloud can change how organizational and trust boundaries are defined and applied. The actual administration of a private cloud environment may be carried out by internal or outsourced staff.
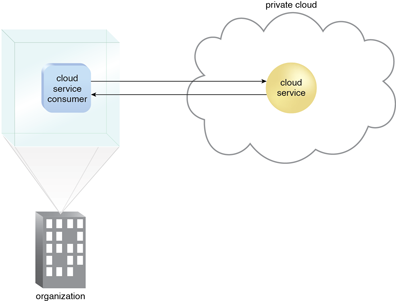
Figure 1 – A cloud service consumer in the organization’s on-premise environment accesses a cloud service hosted on the same organization’s private cloud via a virtual private network.
With a private cloud, the same organization is technically both the cloud consumer and cloud provider (Figure 1). In order to differentiate these roles:
- a separate organizational department typically assumes the responsibility for provisioning the cloud (and therefore assumes the cloud provider role)
- departments requiring access to the private cloud assume the cloud consumer role
It is important to use the terms “on-premise” and “cloud-based” correctly within the context of a private cloud. Even though the private cloud may physically reside on the organization’s premises, IT resources it hosts are still considered “cloud-based” as long as they are made remotely accessible to cloud consumers. IT resources hosted outside of the private cloud by the departments acting as cloud consumers are therefore considered “on-premise” in relation to the private cloud-based IT resources.

