Big Data Patterns, Mechanisms > Mechanisms > Security Engine
Security Engine
![]()
A Big Data platform is a combination of multiple resources, which are provided by different mechanisms, each with its own unique security configuration. This requires developing and maintaining separate security policies and API-based integration.
In a clustered environment, this can become cumbersome and difficult to maintain, especially where data is accessed across the enterprise with varying levels of authorization. Correct access levels need to be consistently configured across all required resources, such as a storage device or a processing engine. Instead of configuring access for each resource individually, a security engine can be used.
As shown in Figure 1, a security engine acts as a single point of contact for securing a Big Data platform, providing authentication, authorization and access auditing features. It acts as a perimeter guard for the cluster with centralized security policy declaration and management, enabling role-based security.
For enhanced data access security, a security engine may provide fine-grained control over how data is accessed from a range of storage devices and assist with addressing regulatory compliance concerns.
A security engine may also integrate with enterprise identity and access management (IAM) systems to enable single sign-on (SSO). Furthermore, security engines provide data confidentiality by enabling data encryption for at-rest (data stored in a storage device) and in-motion (data in transit over a network) data.
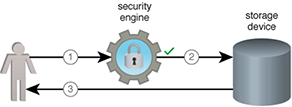
Figure 1 – 1. A user requests some data from a storage device. The request is intercepted by the security engine. 2. The request is successfully authenticated and authorized by the security engine. 3. The storage device returns the requested data.
Related Patterns:
This pattern is covered in BDSCP Module 2: Big Data Analysis & Technology Concepts.
For more information regarding the Big Data Science Certified Professional (BDSCP) curriculum,
visit www.arcitura.com/bdscp.
