Big Data Patterns, Mechanisms > Storage Patterns > Realtime Access Storage
Realtime Access Storage (Buhler, Erl, Khattak)
How can large amounts of data be accessed instantaneously without any delay?

Problem
Solution
Application
Mechanisms
A cluster-based storage device that utilizes random access memory (RAM) as the storage medium is used. By keeping data in memory, the mechanical data seeking operations, such as movement of the read/write head, occur in a disk-based storage device. A memory-based storage device either persists data as key-value pairs across the cluster or provides NoSQL storage. The application of this pattern needs to be carefully planned, as memory-based devices are expensive when compared with their disk-based counterparts.
This pattern is generally applied together with the Streaming Source and High-Velocity Realtime Processing patterns.
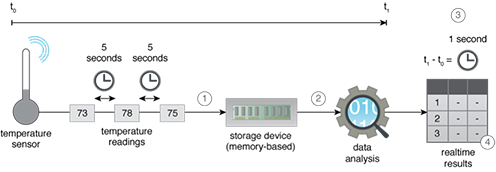
Instead of using a disk-based storage device, a memory-based storage device is used to store high velocity data. The use of memory instead of a disk as the storage medium makes data access considerably faster. Memory-based storage can also be used for continuous or always-on analytics. Furthermore, such a storage strategy is ideal for storing data the needs to be processed recursively, such as in the case of certain machine learning algorithms.
- A temperature sensor emits temperature readings every five seconds, which are stored in a memory-based storage device.
- The data stored on the memory-based storage device is then analyzed.
- The time taken from ingest to analysis amounts to one second.
- This is ideal, as the time lag is only minimal, resulting in realtime results.
This pattern is covered in BDSCP Module 11: Advanced Big Data Architecture.
For more information regarding the Big Data Science Certified Professional (BDSCP) curriculum,
visit www.arcitura.com/bdscp.
The official textbook for the BDSCP curriculum is:
Big Data Fundamentals: Concepts, Drivers & Techniques
by Paul Buhler, PhD, Thomas Erl, Wajid Khattak
(ISBN: 9780134291079, Paperback, 218 pages)
Please note that this textbook covers fundamental topics only and does not cover design patterns.
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

