Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Sharing, Scaling and Elasticity Patterns > Dynamic Scalability
Dynamic Scalability (Erl, Naserpour)
How can IT resources be scaled automatically in response to fluctuating demand?
Problem
It is challenging to equip an IT resource to match its processing requirements. If the demand for the IT resource is below its capacity, then it is under-utilized and if the demand is above its capacity it is over-utilized or unable to meet the demand.
Solution
The IT resource can be integrated with a reactive cloud architecture capable of automatically scaling it horizontally or vertically in response to fluctuating demand.
Application
Dynamic horizontal scaling can be enabled via the use of pools of identical IT resources and components capable of dispersing and retracting workloads across each pool. Dynamic vertical scaling can be enabled via technology capable of swapping IT resource components at runtime.
Mechanisms
Automated Scaling Listener, Cloud Storage Device, Cloud Usage Monitor, Hypervisor, Pay-Per-Use Monitor, Resource Replication, Virtual Server
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
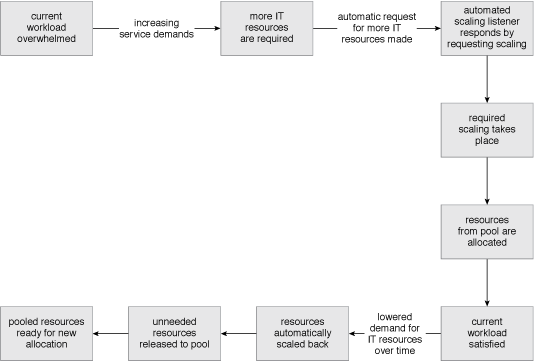
A sample dynamic scaling process.
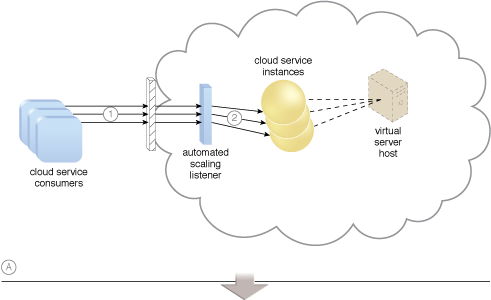
An example of a dynamic scaling architecture involving an automated scaling mechanism (Part I).
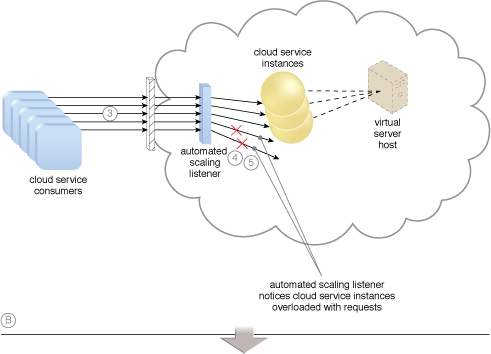
An example of a dynamic scaling architecture involving an automated scaling mechanism (Part II).
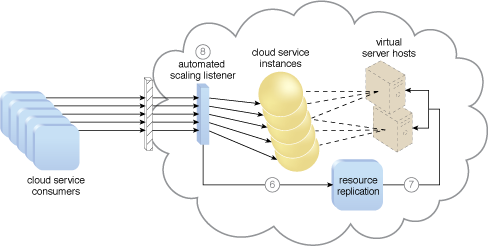
An example of a dynamic scaling architecture involving an automated scaling mechanism (Part III).
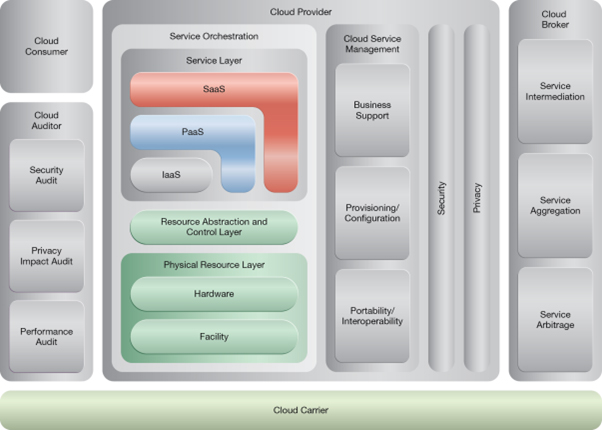
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
This mechanism is covered in CCP Module 4: Fundamental Cloud Architecture.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is covered in:
Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture by Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood,
Ricardo Puttini
(ISBN: 9780133387520, Hardcover, 260+ Illustrations, 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

