Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Reliability, Resiliency and Recovery Patterns > Storage Maintenance Window
Storage Maintenance Window (Erl, Naserpour)
How can access to data in a cloud storage device be preserved during a maintenance outage?

Problem
Hardware maintenance on cloud storage devices can require shutting down the device, resulting in loss of data access and disruption of service.
Solution
An outage prevention system is created to temporarily move the data without interruption during maintenance and other types of outages.
Application
LUN migration is applied to temporarily transfer data to a separate cloud storage device during the maintenance window.
Mechanisms
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
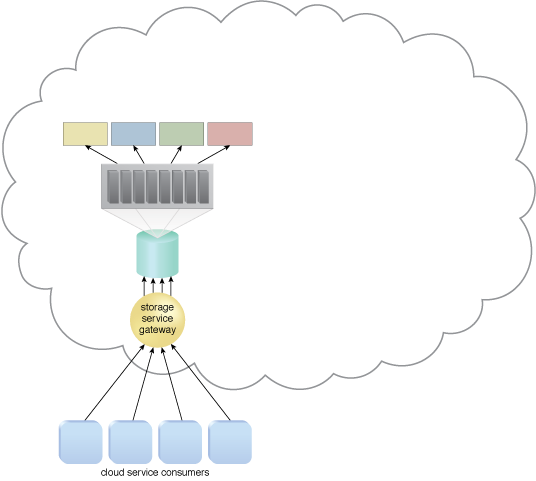
The cloud storage device is scheduled to undergo a maintenance outage.
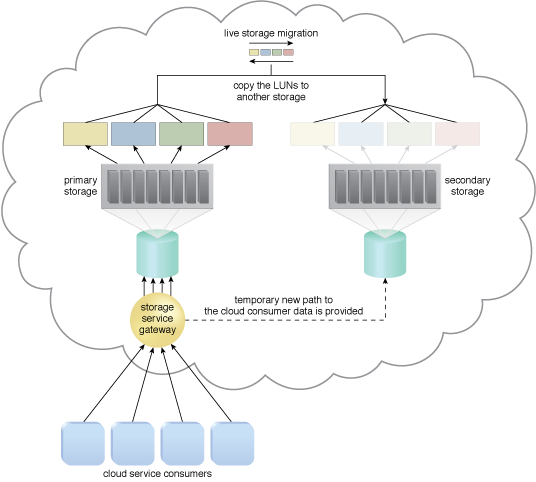
Live storage migration moves the LUNs from the primary storage device to a secondary storage device.
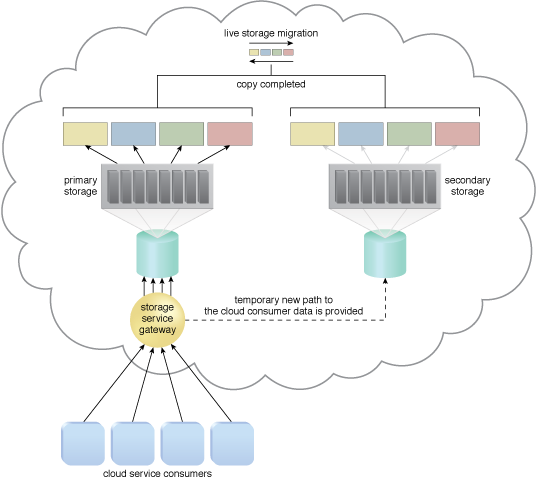
When the LUN’s data has been migrated, requests for the data are forwarded to the duplicate LUNs on the secondary storage device.
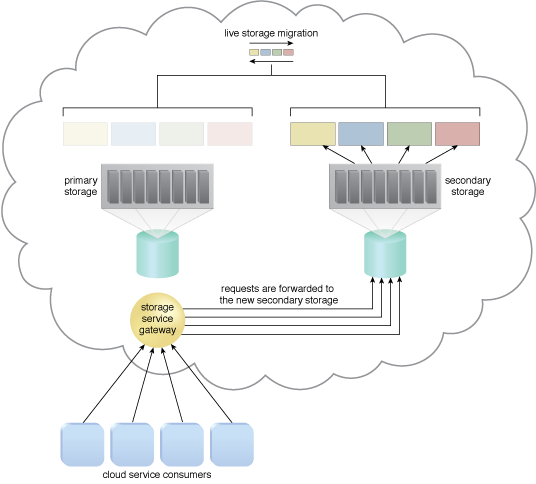
The primary storage is powered off for maintenance.
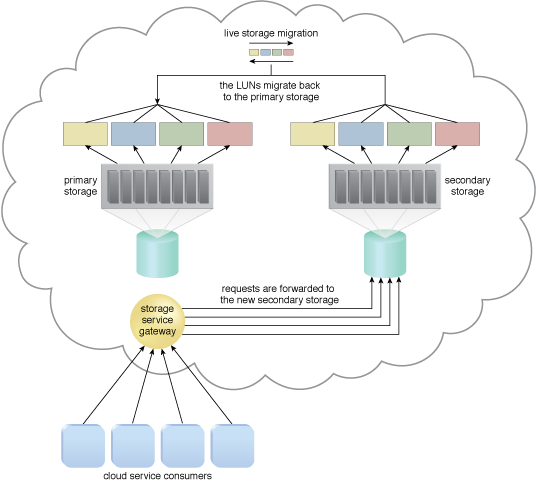
When it is confirmed that the maintenance task on the primary storage device has been completed, the primary storage is brought back online. Live storage migration subsequently restores the LUN data from the secondary storage device to the primary storage device.
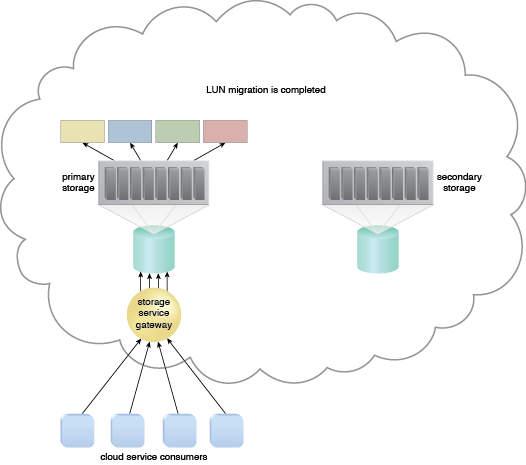
When the LUN migration is completed, all data access requests are forwarded back to the primary storage device.
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
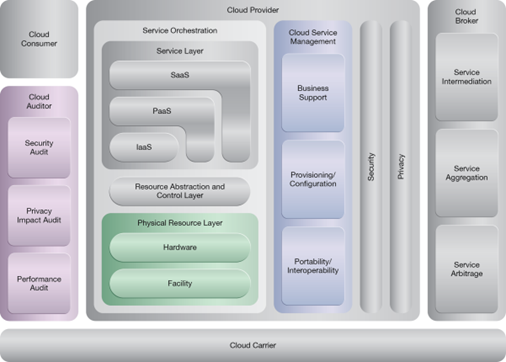
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 5: Advanced Cloud Architecture.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 14: Advanced Cloud Storage.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is covered in:
Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture by Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood,
Ricardo Puttini
(ISBN: 9780133387520, Hardcover, 260+ Illustrations, 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


