Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Mechanisms > A - B > Attestation Service
Attestation Service

An attestation service is responsible for assessing the integrity of cloud compute nodes through techniques introduced by the trusted computing technology and trusted platform modules (TPMs). The TPM creates a hash of a boot component and validates the hash against a set of securely stored values.
A remote attestation service is critical for implementing secure compute platforms in the cloud. It checks whether a platform is launched with known-good firmware and software components, communicates the security trust level or trustworthiness of a platform to consumers, and supports visibility and auditability.
In the figure, the attestation service receives signed attestations from secure boot verification services. The attestation service validates the signatures on boot measurements and makes the attestations available to authenticated administrators, workflow engines and orchestration engines that need to know the security status of a resource before dispatching a workload.
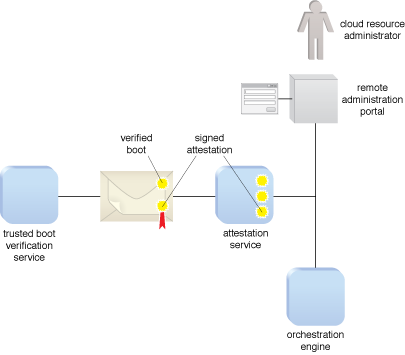
An example of an attestation service.
Related Patterns:
- Cloud Storage Data Placement Compliance Check
- Trust Attestation Service
- Trusted Cloud Resource Pools
This mechanism is covered in CCP Module 7: Fundamental Cloud Security and
in Module 8: Advanced Cloud Security.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is also covered in:
Cloud Computing Design Patterns by Thomas Erl, Robert Cope, Amin Naserpour
(ISBN: 9780133858563, Hardcover, ~ 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


