Microservice and Containerization Patterns > State & Data Access Patterns > Synchronized Cross-Instance Events
Synchronized Cross-Instance Events (Erl, Naserpour)
How can microservice data consistency be achieved across all microservice instances when each microservice instance has its own database instance?

Problem
Solution
Application
A system is introduced to ensure that each microservice instance publishes an event whenever it occurs and that the database instances of the microservice instances subscribed to that event are updated.
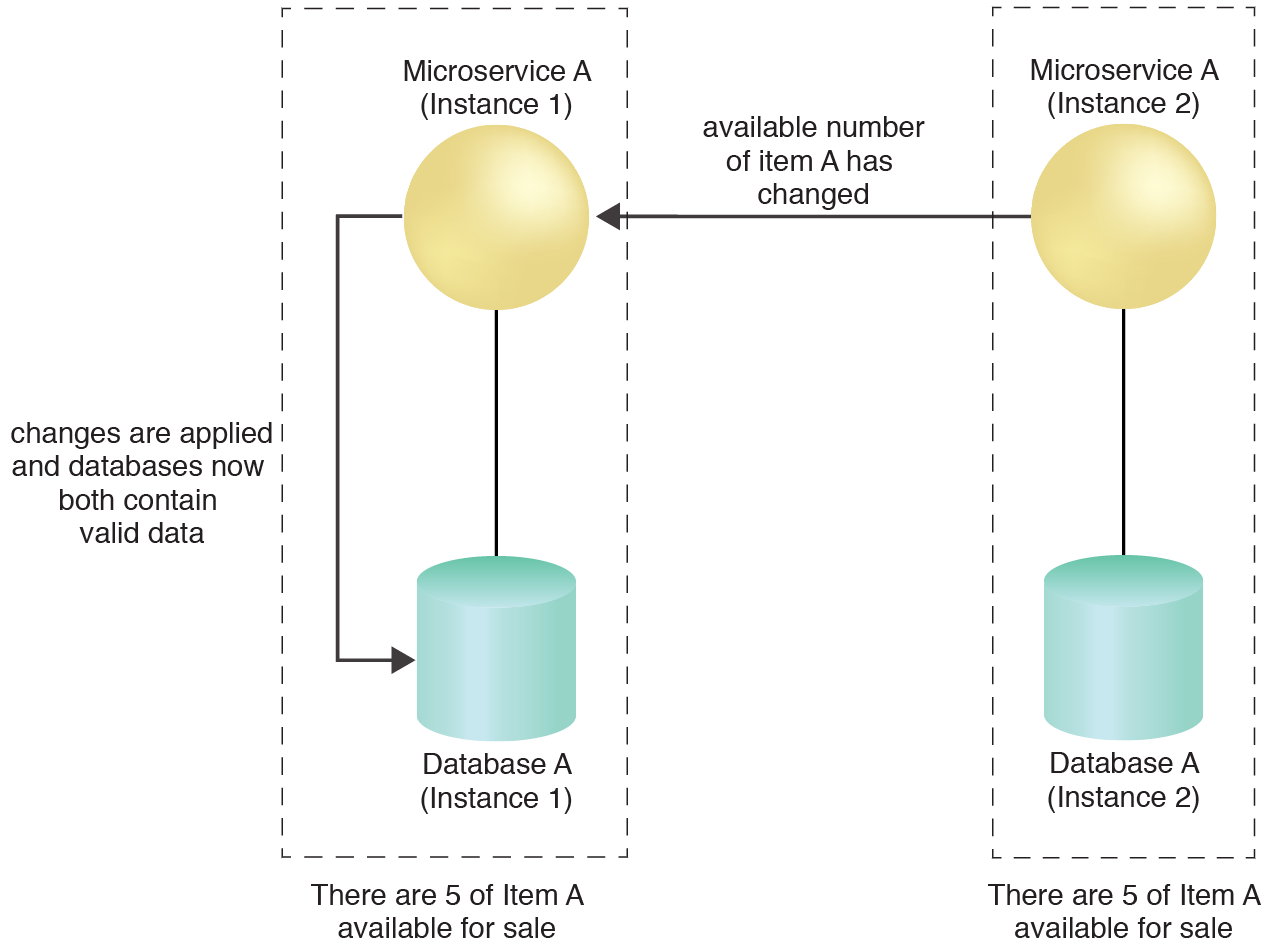
Microservice A (Instance 1) was subscribed to Microservice B (Instance 2) and is therefore notified of the change to Database B (Instance 2). Upon receiving the notification, Microservice A (Instance 1) correspondingly updates Database A (Instance 1).
This pattern is applied by identifying events designing function for subscribing to specific state changes, as explained in the complete pattern description.
This pattern is covered in Module 10: Advanced Microservice Architecture & Containerization..
For more information regarding microservice and containerization courses and accreditation,
visit the Microservice Architect Certification program page..
