Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Data Management and Storage Device Patterns > Cloud Storage Data Placement Compliance Check
Cloud Storage Data Placement Compliance Check (Cope, Erl)
How can cloud consumers ensure data is stored on a cloud storage device is physically located in a region that meets required compliance policies?

Problem
Cloud consumer organizations may need to comply with regulatory data hosting policies that may place specific location requirements upon the storage devices used to host the data. However, when hosting data in a third-party cloud, there may be no way of knowing whether the cloud storage devices used meet these requirements.
Solution
A solution is implemented to monitor the location of a cloud storage device and send notifications should the storage conditions no longer satisfy compliance policies.
Application
The cloud storage data placement auditor mechanism is used to enforce policies defined by the cloud consumer (or cloud provider) on a specific dataset or cloud storage device.
Mechanisms
Attestation Service, Cloud Storage Device, Geotag, Resource Replication, Trusted Platform Module
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
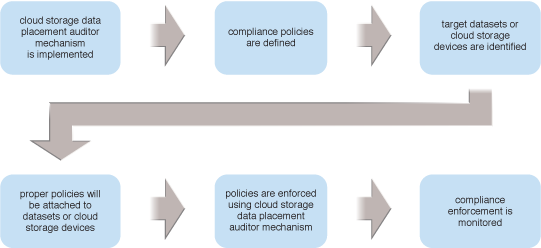
The steps in applying the Cloud Storage Data Placement Compliance Check pattern are illustrated.
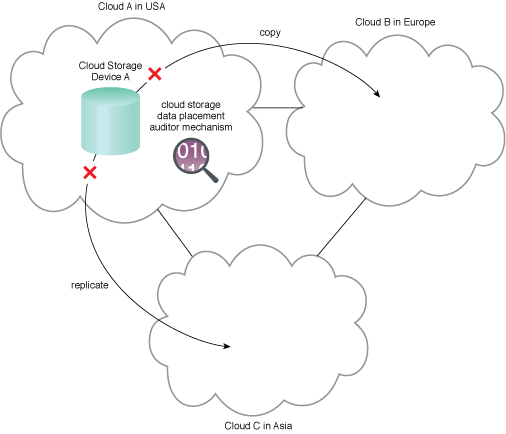
A cloud storage data placement auditor mechanism monitors and enforces policies on Cloud Storage Device A.
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 14: Advanced Cloud Storage.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
The architectural model upon which this design pattern is based is further covered in:
Cloud Computing Design Patterns by Thomas Erl, Robert Cope, Amin Naserpour
(ISBN: 9780133858563, Hardcover, ~ 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

