Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Reliability, Resiliency and Recovery Patterns > Redundant Storage
Redundant Storage (Erl, Naserpour)
How can the reliability and availability of cloud storage devices survive failure conditions?

Problem
When cloud storage devices fail or become inaccessible, cloud consumers are unable to access data and cloud services relying on access to the device may also fail.
Solution
A failsafe system comprised of redundant cloud storage devices is established so that when the primary device fails, the redundant secondary device takes its place.
Application
Data is replicated from the primary storage to the secondary storage device. A storage service gateway is used to redirect data access requests to the secondary storage device, when necessary.
Mechanisms
Cloud Storage Device, Container, Failover System, Resource Replication
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
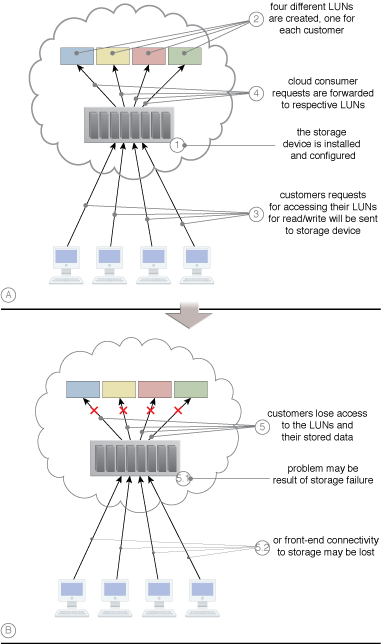
A sample scenario that demonstrates the effects of a failed cloud storage device.
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
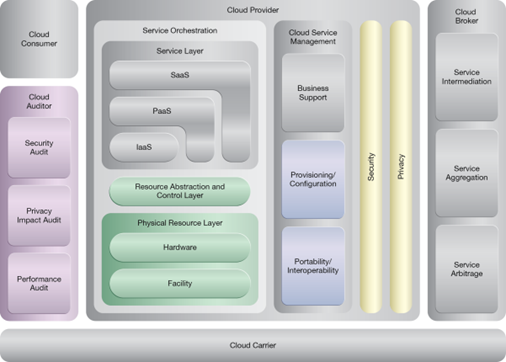
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 5: Advanced Cloud Architecture.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 14: Advanced Cloud Storage.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is covered in:
Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture by Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood,
Ricardo Puttini
(ISBN: 9780133387520, Hardcover, 260+ Illustrations, 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


