Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Monitoring, Provisioning and Administration Patterns > Self-Provisioning
Self-Provisioning (Erl, Naserpour)
How can cloud consumers be empowered to have IT resources provisioned on-demand?

Problem
Manual or semi-automated IT resource provisioning processes required by cloud providers can be time-consuming and inefficient and can impose unnecessary delays and effort upon cloud consumers.
Solution
A self-service portal is established with the ability to interface with back-end systems required for the automated provisioning of IT resources.
Application
In addition to offering front-end controls for cloud consumers to choose IT resources for automated provisioning, the self-service portal is also equipped with the ability to receive a feed of current IT resources that are available for provisioning.
Mechanisms
Audit Monitor, Cloud Usage Monitor, Container, Logical Network Perimeter, Multi-Device Broker, Remote Administration System
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
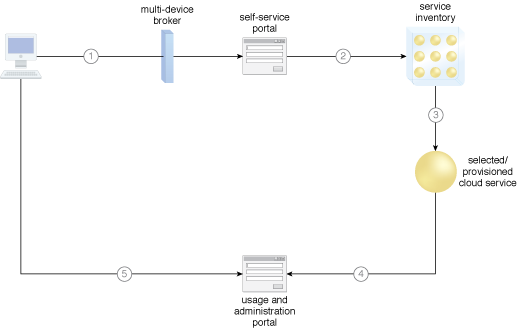
A simple cloud architecture in which both the self-service portal and usage and administration portal play roles in relation to how cloud services are provisioned online.
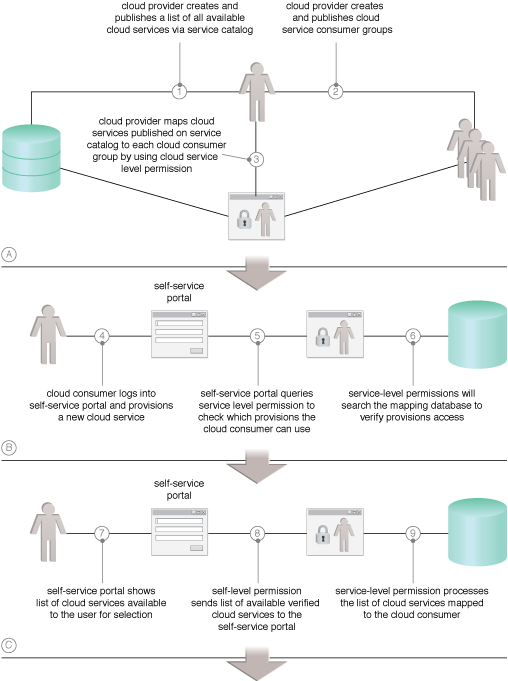
Common steps required to navigate the permission approval process of a self-service portal (Part I).
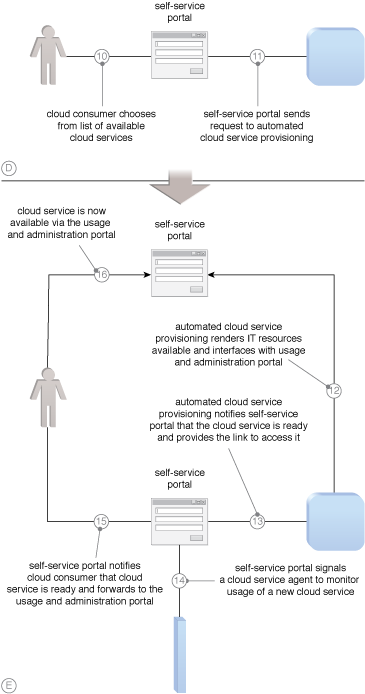
Common steps required to navigate the permission approval process of a self-service portal (Part II).
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
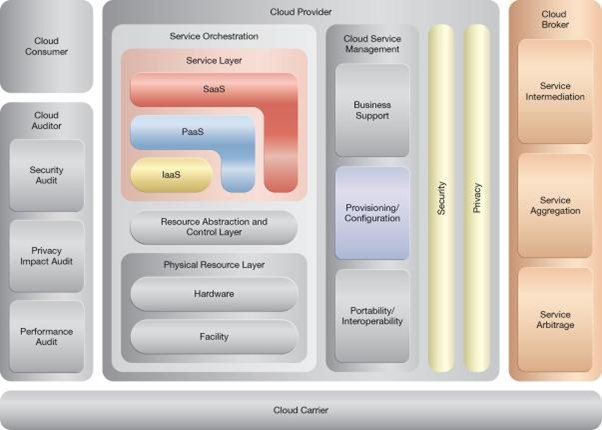
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 4: Fundamental Cloud Architecture.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
