Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Network Security, Identity & Access Management and Trust Assurance Patterns > Independent Cloud Auditing
Independent Cloud Auditing (R. Cope, S. Cope, Erl, Morawala)
How can cloud-hosted IT resources be audited for compliance and SLA requirements when they are not owned or accessible by cloud consumers?

Problem
Assessments for security requirement objectives of confidentiality, integrity, and availability need to be performed by cloud consumers, providers, and third-party participants to ensure legal, security compliance, audit policy, and service level agreement (SLA) requirements are met. However, depending on the cloud service and delivery models, the organization does not own all the IT resources being consumed.
Solution
A specialized auditing approach is implemented in coordination with the cloud consumer, cloud provider, and a third-party cloud auditor.
Application
Auditing implementation, including configuration of security information and event management (SIEM) systems, can be determined based on regulatory compliance requirements and collaboration responsibilities between the cloud consumer, cloud provider, and a third party.
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
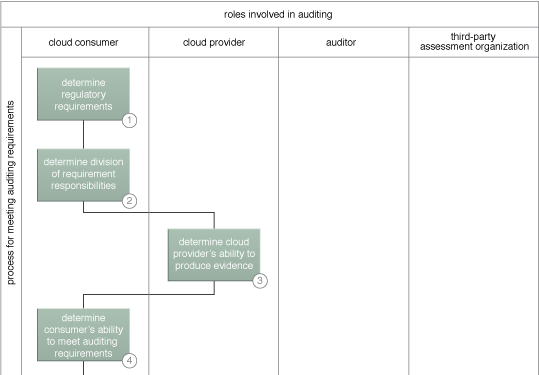
A sample cloud auditing process (Part I).
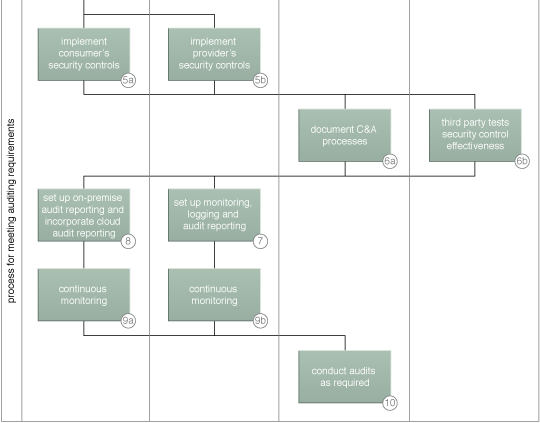
A sample cloud auditing process (Part II).
This mechanism is covered in CCP Module 7: Fundamental Cloud Security and
in Module 8: Advanced Cloud Security.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
The architectural model upon which this design pattern is based is further covered in:
Cloud Computing Design Patterns by Thomas Erl, Robert Cope, Amin Naserpour
(ISBN: 9780133858563, Hardcover, ~ 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


