Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Sharing, Scaling and Elasticity Patterns > Workload Distribution
Workload Distribution (Erl, Naserpour)
How can IT resource over-utilization be avoided?

Problem
IT resources subjected to high volumes of concurrent usage can suffer degraded performance, reduced availability and reliability, and can become susceptible to overall failure.
Solution
The IT resource is horizontally scaled and a load balancing system is used to distribute runtime workloads across multiple IT resources.
Application
Load balancing technology is incorporated into the cloud architecture and configured with appropriate load balancing algorithms to ensure effective workload distribution.
Mechanisms
Audit Monitor, Cloud Storage Device, Cloud Usage Monitor, Container, Hypervisor, Load Balancer, Logical Network Perimeter, Resource Cluster, Resource Replication, Virtual Server
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
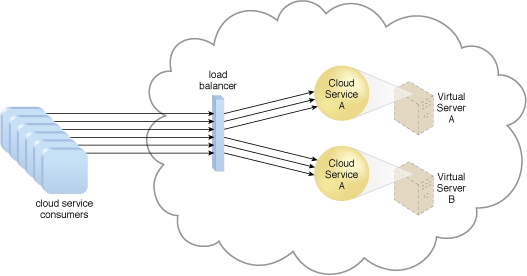
A redundant copy of Cloud Service A is implemented on Virtual Server B. The load balancer intercepts the cloud service consumer requests and directs them to both Virtual Server A and B to ensure even distribution of the workload.
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
This mechanism is covered in CCP Module 4: Fundamental Cloud Architecture.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is covered in:
Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture by Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood,
Ricardo Puttini
(ISBN: 9780133387520, Hardcover, 260+ Illustrations, 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

