Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Sharing, Scaling and Elasticity Patterns > Load Balanced Virtual Switches
Load Balanced Virtual Switches (Erl, Naserpour)
How can workloads be dynamically balanced on physical network connections to prevent bandwidth bottlenecks?

Problem
When network traffic on the uplink port for a virtual switch increases, it can cause delays, performance issues and packet loss because the affected virtual servers are sending and receiving traffic via only one uplink.
Solution
Network traffic is balanced across multiple uplinks between the virtual and physical networks.
Application
Extra network interface cards are added to the physical host to accommodate the virtual switch that is configured with multiple physical uplinks.
Mechanisms
Cloud Usage Monitor, Hypervisor, Load Balancer, Logical Network Perimeter, Physical Uplink, Resource Replication, Virtual Infrastructure Manager, Virtual Server, Virtual Switch
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
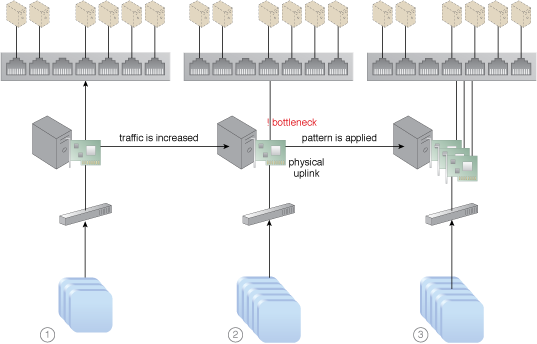
The addition of network interface cards and physical uplinks allows network workloads to be balanced.
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
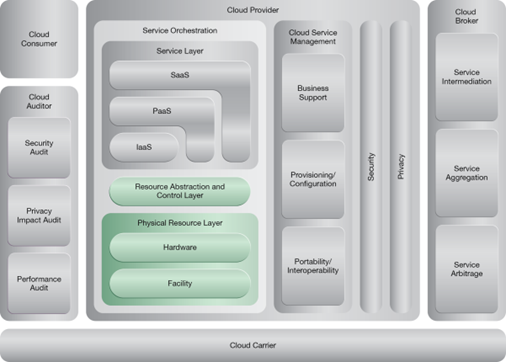
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 5: Advanced Cloud Architecture.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 17: Advanced Cloud Virtualization.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is covered in:
Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture by Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood,
Ricardo Puttini
(ISBN: 9780133387520, Hardcover, 260+ Illustrations, 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


