Big Data Patterns, Mechanisms > Data Processing Patterns > Large-Scale Graph Processing
Large-Scale Graph Processing (Buhler, Erl, Khattak)
How can algorithms that require iterative processing of a large dataset that may or may not contain connected entities be processed in an efficient and timely manner?
Problem
Solution
Application
Mechanisms
A graph processing engine, such as bulk synchronous parallel (BSP), is used, which internally implements a message-passing functionality to provide a method of communication between entities that are spread across multiple logical processors within the cluster. Such a processing engine further persists the entity state in memory. Keeping state data in memory provides a means for restarting the next iteration of the job immediately without having to initialize a new processing job.
When faced with extremely large datasets, the performance gains achieved from the application of the Large-Scale Graph Processing pattern may deteriorate, for the intermediate entity state may need to be stored to disk due to memory constraints. Also, due to the specialized nature of the processing engine, graph processing engine-specific implementations for all algorithms may not be available.
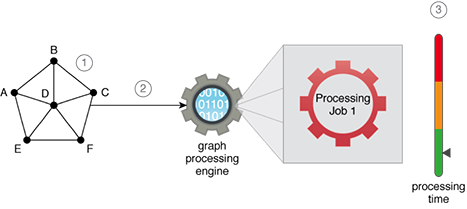
Data is processed using a distributed processing engine that makes use of stateful data processing techniques in support of executing iteration-based algorithms. This helps with massively speeding up the execution time of an iterative algorithm.
- A shortest path algorithm needs to be applied to a dataset, comprising a set of connected entities, to find the shortest path between Entities A and F.
- A graph processing engine is used to implement the shortest path calculation algorithm that is able to execute the entire algorithm within a single processing job in order to find the shortest path.
- The entire execution of the shortest path algorithm takes a short time to complete.
This pattern is covered in BDSCP Module 11: Advanced Big Data Architecture.
For more information regarding the Big Data Science Certified Professional (BDSCP) curriculum,
visit www.arcitura.com/bdscp.
The official textbook for the BDSCP curriculum is:
Big Data Fundamentals: Concepts, Drivers & Techniques
by Paul Buhler, PhD, Thomas Erl, Wajid Khattak
(ISBN: 9780134291079, Paperback, 218 pages)
Please note that this textbook covers fundamental topics only and does not cover design patterns.
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

