Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Data Management and Storage Device Patterns > Virtual Disk Splitting
Virtual Disk Splitting (Cope, Erl)
How can a virtual disk be moved to another location that is either in the same cloud storage device or in a different cloud storage device?

Problem
Moving a virtual disk to a different location is sometimes required, but when the destination location is incompatible, the move may not be possible losing functionality.
Solution
A solution is implemented that ensures that the destination location for a virtual disk is compatible prior to the attempted move.
Application
The virtual disk and its related files (log files, snapshots) are moved to a location that matches the virtual disk’s requirements.
Mechanisms
Cloud Storage Device, Hypervisor, Virtual Disk, Virtual Infrastructure Manager, Virtualization Monitor
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
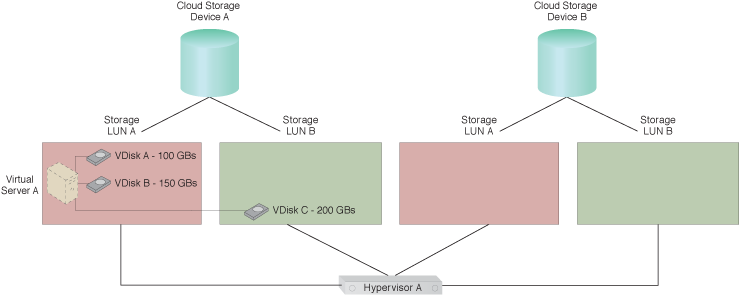
Virtual Disk C has been migrated to LUN B by a live VM migration mechanism to accommodate Application A’s increasing requirements.
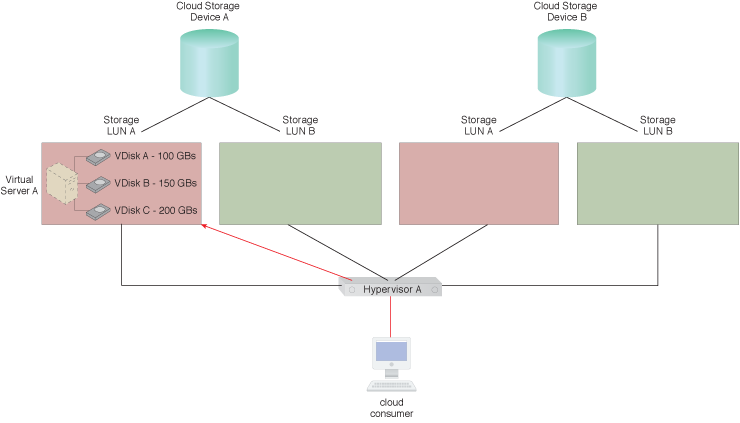
Cloud consumer requests for Application A on VDisk C are being sent to LUN A.
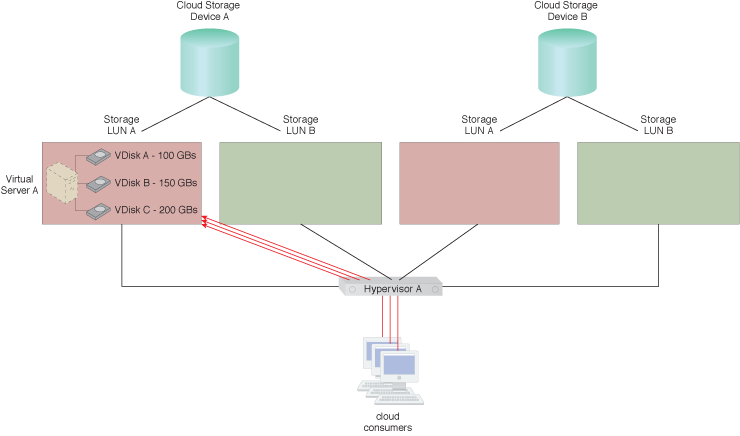
The number of cloud consumer requests being sent to LUN A increases.
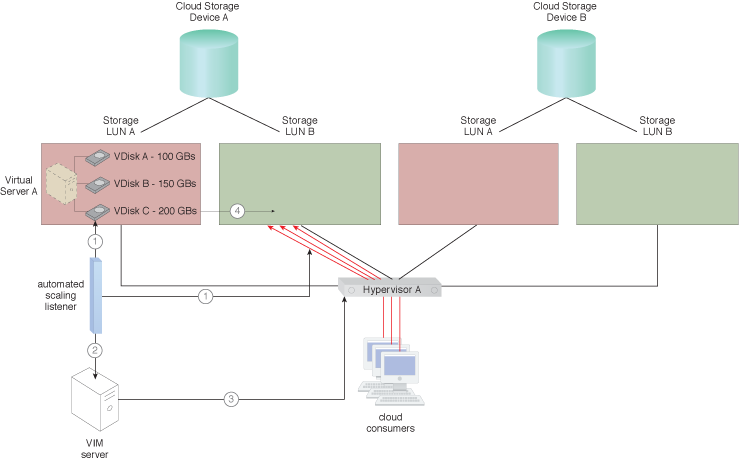
The steps for applying this pattern are shown.
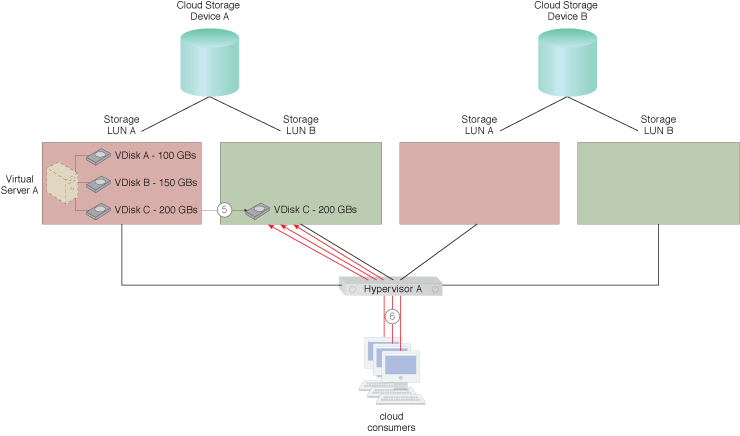
The steps for applying this pattern are shown.
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 17: Advanced Cloud Virtualization.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
The architectural model upon which this design pattern is based is further covered in:
Cloud Computing Design Patterns by Thomas Erl, Robert Cope, Amin Naserpour
(ISBN: 9780133858563, Hardcover, ~ 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

