Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Reliability, Resiliency and Recovery Patterns > Synchronized Operating State
Synchronized Operating State (Erl, Naserpour)
How can the availability and reliability of virtual servers be ensured when high availability and clustering technology is unavailable?

Problem
A cloud consumer may be prevented from utilizing high availability and clustering technology for its virtual servers or operating systems, thereby making them more vulnerable to failure.
Solution
A composite failover system is created to not rely on clustering or high availability features but instead use heartbeat messages to synchronize virtual servers.
Application
The heartbeat messages are processed by a specialized service agent and are exchanged between hypervisors, the hypervisor and virtual server, and the hypervisor and VIM.
Mechanisms
Cloud Storage Device, Failover System, Hypervisor, Resource Replication, State Management Database, Virtual Server
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
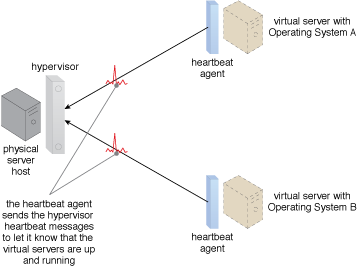
Special heartbeat agents are employed to monitor heartbeat messages exchanged between the servers.
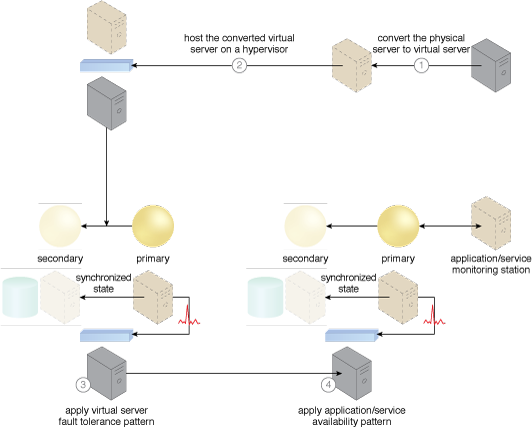
The cloud architecture resulting from the application of this pattern.
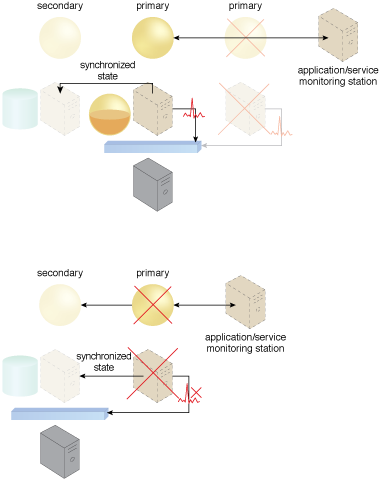
When the primary virtual server fails, along with its hosted cloud service, heartbeat messages are no longer transmitted. As a result, the hypervisor recognizes the failure and switches activity to the secondary virtual server that maintains the synchronized state. After the primary virtual server is back online, the hypervisor creates a new secondary for the new primary, and proceeds to save it as a synchronized non-active state.
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
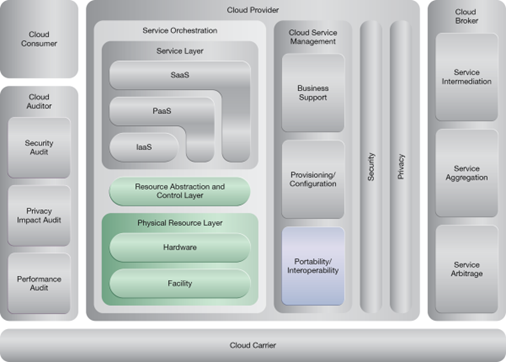
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 5: Advanced Cloud Architecture.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
