Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Sharing, Scaling and Elasticity Patterns > Cross-Storage Device Vertical Tiering
Cross-Storage Device Vertical Tiering (Erl, Naserpour)
How can the vertical scaling of data processing be carried out dynamically?

Problem
Increasing the processing capacity of data stored on cloud storage devices generally requires the manual vertical scaling of the device, which is inefficient and potentially wasteful.
Solution
A system is established whereby the vertical scaling of data processing can be carried out dynamically across multiple cloud storage devices.
Application
Using pre-defined capacity thresholds, LUN migration is used to dynamically move LUN disks between cloud storage devices with different capacities.
Mechanisms
Audit Monitor, Automated Scaling Listener, Cloud Storage Device, Cloud Usage Monitor, Pay-Per-Use Monitor
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
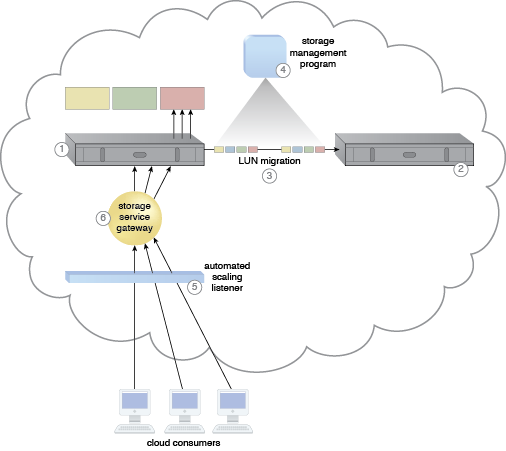
A cloud architecture resulting from the application of the Cross-Storage Device Vertical Tiering pattern (Part I).
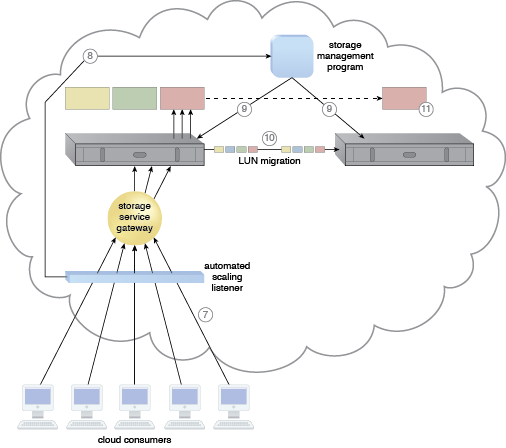
A cloud architecture resulting from the application of the Cross-Storage Device Vertical Tiering pattern (Part II).
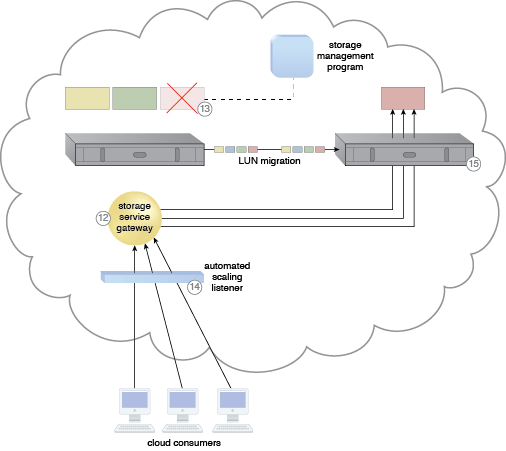
A cloud architecture resulting from the application of the Cross-Storage Device Vertical Tiering pattern (Part III).
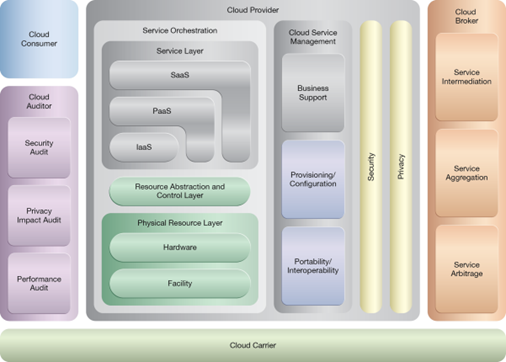
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 5: Advanced Cloud Architecture.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 14: Advanced Cloud Storage.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is covered in:
Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture by Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood,
Ricardo Puttini
(ISBN: 9780133387520, Hardcover, 260+ Illustrations, 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


