Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Sharing, Scaling and Elasticity Patterns > Service State Management
Service State Management (Erl, Naserpour)
How can stateful cloud services be optimized to minimize runtime IT resource consumption?

Problem
A cloud service designed to place significant data into memory for prolonged periods can consume excessive amounts of runtime processing, thereby unreasonably taxing the overall cloud infrastructure and imposing additional usage costs on cloud consumers.
Solution
The cloud service is designed to integrate with a state management system allowing it to defer state data at runtime when necessary so as to minimize its IT resource consumption.
Application
A state management system requires a cloud storage device capable of temporarily holding and releasing state data exchanged by the cloud service. The cloud service itself needs to be equipped with logic to determine when and how to release and retrieve state data.
Mechanisms
Cloud Storage Device, Cloud Usage Monitor, Hypervisor, Pay-Per-Use Monitor, Resource Replication, State Management Database, Virtual Server
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
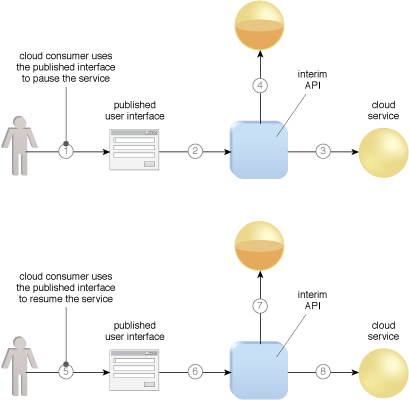
A sample scenario in which cloud service state data is manually deferred and restored.
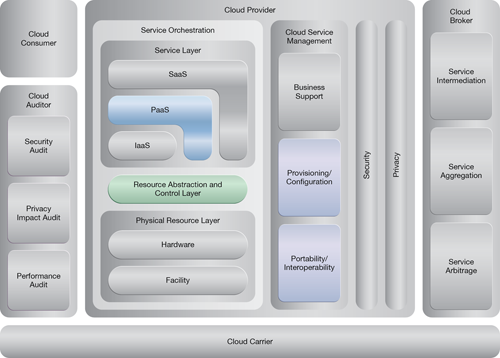
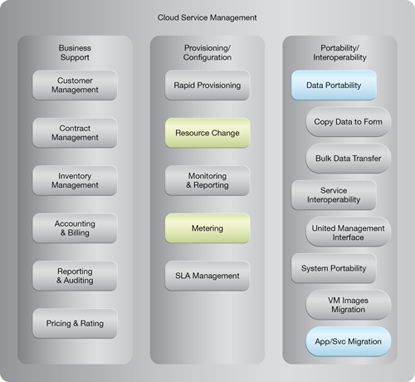
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 4: Fundamental Cloud Architecture.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
