DevOps Mechanisms, Metrics, Tools > Metrics > Availability
Availability
This metric is dedicated to measuring the availability of a software program. Depending on the nature of the software, availability mechanisms may be built into its design or its surrounding technology architecture. Existing infrastructure resources, such as failover or storage replication, may also be utilized to enhance a program’s availability.

Availability metrics measured at different phases.
Availability is often expressed in percentage values comprised of 9s. For example, 99% (also known as 2 nine) or 99.999% (also known as 5 nine). Sometimes availability is defined by the amount of time that an application is available within a given extended period, such as a day or week. This time value generally accounts for unplanned outages only. The following table shows examples of different availability levels based on percentage and time.
| Availability % | Downtime per Year | Downtime per Month | Downtime per Week | Downtime per Day |
| 90% (“one nine”) | 36.5 days | 72 hours | 16.8 hours | 2.4 hours |
| 95% (“one and a half nines”) | 18.25 days | 36 hours | 8.4 hours | 1.2 hours |
| 97% | 10.96 days | 21.6 hours | 5.04 hours | 43.2 minutes |
| 98% | 7.30 days | 14.4 hours | 3.36 hours | 28.8 minutes |
| 99% (“two nines”) | 3.65 days | 7.20 hours | 1.68 hours | 14.4 minutes |
| 99.5% (“two and a half nines”) | 1.83 days | 3.60 hours | 50.4 minutes | 7.2 minutes |
| 99.80% | 17.52 hours | 86.23 minutes | 20.16 minutes | 2.88 minutes |
| 99.9% (“three nines”) | 8.76 hours | 43.8 minutes | 10.1 minutes | 1.44 minutes |
| 99.95% (“three and a half nines”) | 4.38 hours | 21.56 minutes | 5.04 minutes | 43.2 seconds |
| 99.99% (“four nines”) | 52.56 minutes | 4.38 minutes | 1.01 minutes | 8.64 seconds |
| 99.995% (“four and a half nines”) | 26.28 minutes | 2.16 minutes | 30.24 seconds | 4.32 seconds |
| 99.999% (“five nines”) | 5.26 minutes | 25.9 seconds | 6.05 seconds | 864.3 milliseconds |
| 99.9999% (“six nines”) | 31.5 seconds | 2.59 seconds | 604.8 milliseconds | 86.4 milliseconds |
| 99.99999% (“seven nines”) | 3.15 seconds | 262.97 milliseconds | 60.48 milliseconds | 8.64 milliseconds |
| 99.999999% (“eight nines”) | 315.569 milliseconds | 26.297 milliseconds | 6.048 milliseconds | 0.864 milliseconds |
| 99.9999999% (“nine nines”) | 31.5569 milliseconds | 2.6297 milliseconds | 0.6048 milliseconds | 0.0864 milliseconds |
The availability and uptime of a software program are defined using the following values:
- Non-Operational Time – The time that a software program is unavailable or does not need to be available (for example, a software program that is only required to be available during business hours). If the program fails on Saturday and is recovered by Sunday night, the solution’s availability is not impacted because the outage occurs outside of its operational time.
- Operational Time – The timeframe during which a software program is expected to be operational and available. As per the previous example, a program may only be operational during business hours (9:00am to 5:00pm, Monday to Friday).
- Uptime – The amount of time that a software program is available and operational. For example, if a program fails on Wednesday before 9:00am and is only recovered after 7:00pm that day, its uptime for that week is considered to be one day less than usual, depending on its operational time.
- Planned Downtime – The time scheduled for maintenance, upgrades or changes, such as the replacement of hardware or supporting infrastructure resources.
- Unplanned Downtime – Any downtime that occurs that is not planned.
The following figure illustrates how these values relate.
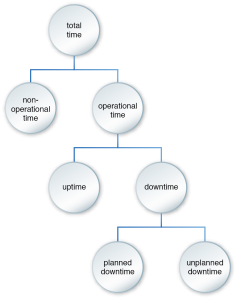
How the values used to calculate availability relate to each other.
The availability of the individual components, services or parts of a greater system can be measured based on either of the following formulas. (The MTBF and MTTR metrics are described later in this section.)

This pattern is covered in DevOps Module 2: DevOps in Practice.
For more information regarding DevOps and accreditation,
visit the DevOps Certification program page.
