Big Data Patterns, Mechanisms > Storage Patterns > Confidential Data Storage
Confidential Data Storage (Buhler, Erl, Khattak)
How can data stored in a Big Data solution environment be kept private so that only the intended client is able to read it?

Problem
Solution
Application
Mechanisms
A security engine is utilized that performs the encryption and decryption of data. Based on the confidentiality requirements, both raw and processed may need to be encrypted. Some NoSQL storage devices may also provide a means for automatic encryption and decryption of stored data.
The application of the Confidential Data Storage pattern can introduce data access latency and increase computational resource usage due to the added the processing requirements of encryption and decryption of data. This requires striking a balance between how long it takes for the algorithm to encrypt/decrypt data and the strength of the produced cipher text.
This pattern is generally applied together with the Centralized Access Management pattern to further protect against unauthorized data access. This way, only users with the right credentials can access the data.
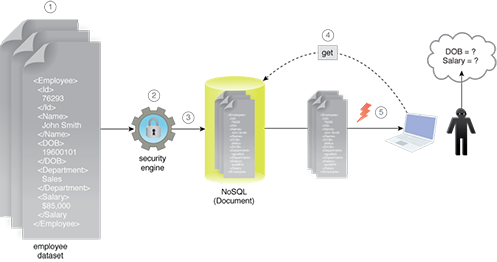
Data that needs to be kept confidential is encrypted, and the encrypted data is then saved in a storage device. When the data needs to be read, it is decrypted first, provided that the client possesses the correct decryption key. This ensures confidentiality for both data-at-rest and data-in-motion.
- An XML dataset contains private data regarding employees, including date of birth and salary.
- The dataset is encrypted using a security engine.
- The encrypted dataset is then stored in a document NoSQL database.
- A malicious user accesses the dataset via the REST interface of the database.
- The database returns the dataset, which the malicious user is unable to parse because the data is encrypted.
This pattern is covered in BDSCP Module 11: Advanced Big Data Architecture.
For more information regarding the Big Data Science Certified Professional (BDSCP) curriculum,
visit www.arcitura.com/bdscp.
The official textbook for the BDSCP curriculum is:
Big Data Fundamentals: Concepts, Drivers & Techniques
by Paul Buhler, PhD, Thomas Erl, Wajid Khattak
(ISBN: 9780134291079, Paperback, 218 pages)
Please note that this textbook covers fundamental topics only and does not cover design patterns.
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

