Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Sharing, Scaling and Elasticity Patterns > Elastic Disk Provisioning
Elastic Disk Provisioning (Erl, Naserpour)
How can the billing of cloud storage be based on actual, fluctuating storage consumption?

Problem
When cloud providers charge for fixed-disk storage allocation, the billing is based on the capacity of the disks, not their actual usage. As a result, cloud consumers are generally billed for more storage than they consume.
Solution
A dynamic storage provisioning system is established to dynamically allocate and remove (and collect billing data for) storage space at a granular level.
Application
Thin provisioning and dynamic allocation technology is used with cloud storage monitors to enable elastic storage space provisioning and the measuring of usage data for billing purposes.
Mechanisms
Cloud Storage Device, Cloud Usage Monitor, Container, Hypervisor, Pay-Per-Use Monitor, Resource Replication, Virtual Server
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
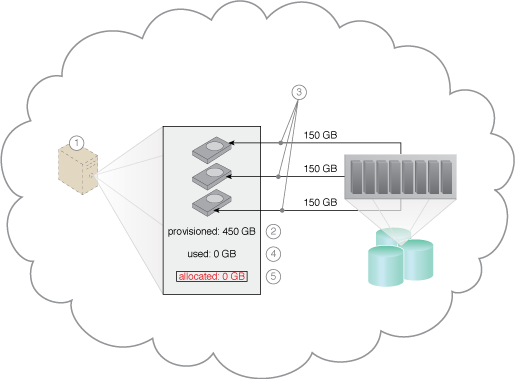
A scenario based on the use of a dynamic-disk allocation based provisioning model.
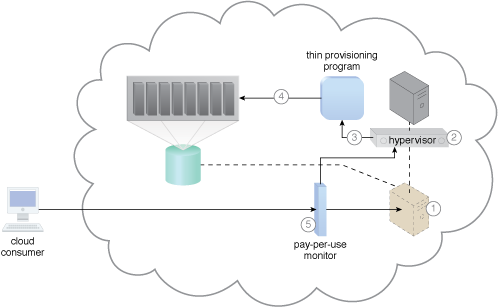
A sample cloud architecture resulting from the application of the Elastic Disk Provisioning pattern.
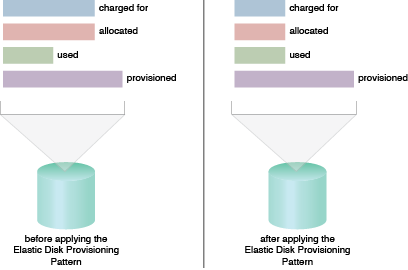
The fixed-disk allocation based provisioning model compared to the dynamic disk provisioning model.
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 5: Advanced Cloud Architecture.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is covered in:
Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture by Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood,
Ricardo Puttini
(ISBN: 9780133387520, Hardcover, 260+ Illustrations, 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

