Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Sharing, Scaling and Elasticity Patterns > Elastic Network Capacity
Elastic Network Capacity (Erl, Naserpour)
How can network bandwidth be allocated to align with actual usage requirements?
Problem
Network bandwidth is often fixed, resulting in performance bottlenecks, runtime exceptions and failure when bandwidth capacity is reached.
Solution
A system is established to dynamically increase or decrease the amount of network ports or network bandwidth in response to actual bandwidth usage.
Application
Cloud consumer network traffic is isolated and each cloud consumer is allocated its own network ports which are retrieved from and returned to a network pool, as per usage requirements.
Mechanisms
Automated Scaling Listener, Cloud Usage Monitor, Container, Hypervisor, Logical Network Perimeter, Pay-Per-Use Monitor, Resource Replication, Virtual Server
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
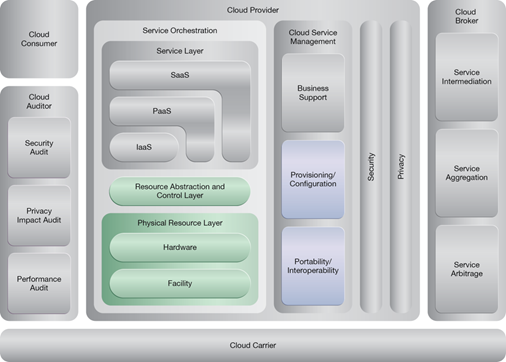
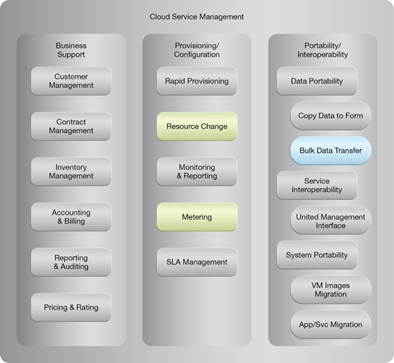
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 5: Advanced Cloud Architecture.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is covered in:
Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture by Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood,
Ricardo Puttini
(ISBN: 9780133387520, Hardcover, 260+ Illustrations, 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.

