Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Mechanisms > T - Z > Virtual Private Cloud
Virtual Private Cloud

The virtual private cloud (VPC) is the segmentation of a public cloud service provider’s multitenant environment to support private cloud computing. The VPC provides secure data transfer between an organization’s on-premise and public cloud provider, ensuring isolated boundaries from every other customer’s data both in transit and inside the cloud provider’s network. Figure 1 shows an on-premise network connected to a VPC.
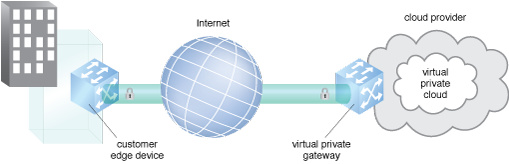
Figure 1 – An example of an on-premise network connected to a VPC.
A VPC allows an organization to provision a cloud on an isolated segment of the cloud provider’s scalable infrastructure where the organization can specify and control their own virtual networking topology. A VPC further allows an organization to configure a custom network topology, as well as manage IP routing and security.
Advantages of VPCs include flexibility for placing workloads on premise, off premise, or both. The VPC architecture enables full management control and integration of resources contained both on premise and in the cloud. This flexibility can be useful when considering certain industry compliance requirements.
Related Patterns:
This mechanism is covered in CCP Module 7: Fundamental Cloud Security and
in Module 8: Advanced Cloud Security.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
The architectural model upon which this design pattern is based is further covered in:
Cloud Computing Design Patterns by Thomas Erl, Robert Cope, Amin Naserpour
(ISBN: 9780133858563, Hardcover, ~ 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


