Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Mechanisms > C > Cloud Consumer Gateway
Cloud Consumer Gateway

The cloud consumer gateway (CCG) is a secure network router anchored on the cloud consumer side of a cloud provider connection. The CCG is a hardware or software-based appliance located on the consumer premises that serves as a bridge between local networks and remote cloud-based networks. Optimally, gateway encryption is managed by the cloud consumer and is required by many industry compliance regulations.
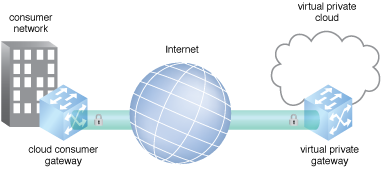
Figure 1 – An example of an on-premise cloud consumer gateway connected to a cloud.
In Figure 1, a CCG is established at the cloud consumer side and connected to a virtual private cloud (VPC) on the cloud provider side using encryption. To protect against a loss of connectivity if the consumer gateway fails, a second VPN connection can be established for traffic balancing or failover to a warm standby. If a firewall is in place between the Internet and the consumer gateway, rules must be configured to establish the VPN tunnels.
Related Patterns:
This mechanism is covered in CCP Module 7: Fundamental Cloud Security and
in Module 8: Advanced Cloud Security.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is also covered in:
Cloud Computing Design Patterns by Thomas Erl, Robert Cope, Amin Naserpour
(ISBN: 9780133858563, Hardcover, ~ 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


