Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Sharing, Scaling and Elasticity Patterns > Dynamic Data Normalization
Dynamic Data Normalization (Erl, Naserpour)
How can redundant data within cloud storage devices be automatically avoided?

Problem
Cloud consumers may store large volumes of redundant data within cloud storage devices, thereby bloating the storage architecture and compromising data access performance.
Solution
Data received by cloud consumers is automatically normalized so that redundant data is avoided and cloud storage device capacity and performance is optimized.
Application
Data de-duplication technology is used to detect and eliminate redundant data at block or file-based levels.
Mechanisms
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
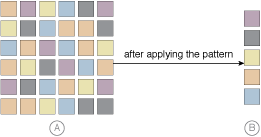
In Part A, datasets containing redundant data unnecessarily bloat data storage. The Dynamic Data Normalization pattern results in the constant and automatic streamlining of data as shown in Part B, regardless of how denormalized the data received from the cloud consumer is.
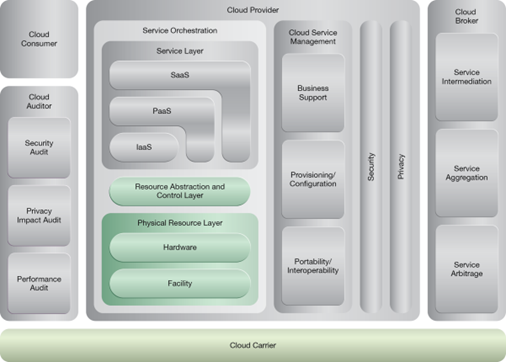
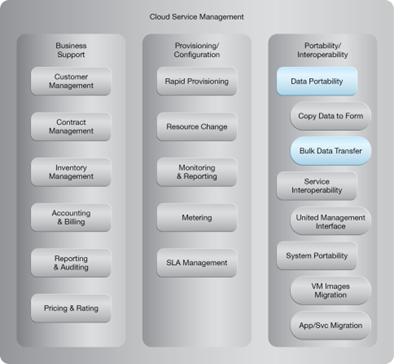
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 5: Advanced Cloud Architecture.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This pattern is covered in CCP Module 14: Advanced Cloud Storage.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
This cloud computing mechanism is covered in:
Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture by Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood,
Ricardo Puttini
(ISBN: 9780133387520, Hardcover, 260+ Illustrations, 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


