Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Basics > Cloud Characteristics > Multitenancy (and Resource Pooling)
Multitenancy (and Resource Pooling)
The characteristic of a software program that enables an instance of the program to serve different consumers (tenants) whereby each is isolated from the other, is referred to as multitenancy. A cloud provider pools its IT resources to serve multiple cloud service consumers by using multitenancy models that frequently rely on the use of virtualization technologies. Through the use of multitenancy technology, IT resources can be dynamically assigned and reassigned, according to cloud service consumer demands.
Resource pooling allows cloud providers to pool large-scale IT resources to serve multiple cloud consumers. Different physical and virtual IT resources are dynamically assigned and reassigned according to cloud consumer demand, typically followed by execution through statistical multiplexing. Resource pooling is commonly achieved through multitenancy technology, and therefore encompassed by this multitenancy characteristic.
Figures 1 and 2 illustrate the difference between single-tenant and multitenant environments.
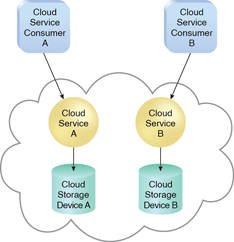
Figure 1 – In a single-tenant environment, each cloud consumer has a separate IT resource instance.
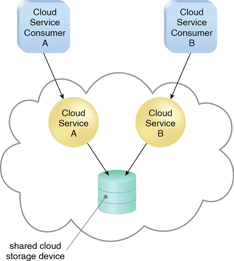
Figure 2 – In a multitenant environment, a single instance of an IT resource, such as a cloud storage device, serves multiple consumers.
As illustrated in Figure 1, multitenancy allows several cloud consumers to use the same IT resource or its instance while each remains unaware that it may be used by others.

