Big Data Patterns, Mechanisms > Mechanisms > Data Governance Manager
Data Governance Manager
![]()
Data governance controls the management of the data lifecycle to ensure that quality data is available in a controlled, secure and timely fashion. Data governance helps ensure regulatory compliance, risk management and the establishment of data lineage.
In a Big Data environment, the variety characteristic coupled with unknown access scenarios can make data governance a challenging task. A data governance manager provides the means for performing various data governance tasks in a centralized manner (Figure 1).
A data governance manager provides information on:
- serialization engine
- compression engine
- where the dataset resides
- who the data owner/steward is
- what the format of the data is
- when the dataset was acquired
- the source of the dataset
- expiry date (if any)
- schema information via metadata search
- a lineage viewer for establishing provenance
In essence, a data governance manager supports data lifecycle management through:
- the authoring of data retention and eviction policies
- the establishment of security policies that specify the conditions under which encryption is applied to a dataset or specific fields of a dataset
- the creation of policies that establish disaster recovery management procedures
Furthermore, a data governance manager can provide information on the level of trust and sensitivity of data. This information includes whether or not the data can be stored in a cloud environment, as well as any geographical limitations for data persistence.
To ensure enhanced data confidentiality and privacy within a cluster, an advanced data governance manager may further enable fine-grained control over data storage by specifying which nodes can store which types of datasets.
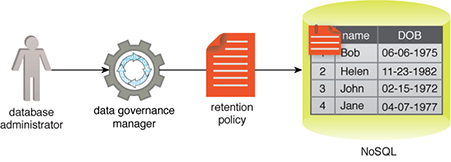
Figure 1 – A database administrator needs to attach a data retention policy to a dataset. A data governance manager can be used to author the retention policy, which is then attached to the relevant dataset.
Related Patterns:
This pattern is covered in BDSCP Module 2: Big Data Analysis & Technology Concepts.
For more information regarding the Big Data Science Certified Professional (BDSCP) curriculum,
visit www.arcitura.com/bdscp.
