Cloud Computing Patterns, Mechanisms > Network Security, Identity & Access Management and Trust Assurance Patterns > Secure Connection for Scaled VMs
Secure Connection for Scaled VMs (Cope, Erl)
How can connections be scaled to protect dynamically scaled VMs in a way that mitigates cloud provider lock-in?

Problem
When scaling cloud resources, differences between cloud consumer on-premise firewall and multiple cloud provider firewall and network protection offerings can make it difficult to configure secure networking.
Solution
A system can be established by controlling network traffic moving in and out of the VM using firewall agents or operating system firewalls. This will create a portable security solution that is location independent and scales as VMs are created.
Application
Using firewall agents or operating system-based firewalls, VMs can be pre-configured with a baseline of firewall policy, including VPN configuration, so that when VMs are created or live migrated in a cloud burst or other scaling activity, the associated firewall is also created or live migrated and pre-configured with firewall policy.
Compound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
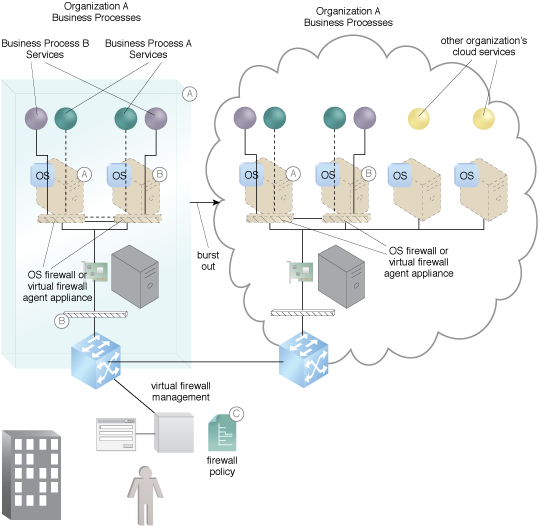
An OS or virtual agent firewall connects Business Process A’s services via a VPN (A). An OS or virtual agent firewall connects Business Process B’s services via a VPN (B). They are all managed by a policy-driven firewall management system capable of managing multiple OS-type firewalls or firewall agents (C).
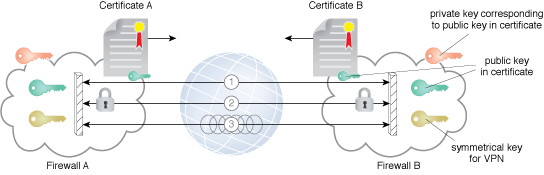
An example of the establishment of a VPN.
This mechanism is covered in CCP Module 7: Fundamental Cloud Security and
in Module 8: Advanced Cloud Security.
For more information regarding the Cloud Certified Professional (CCP) curriculum, visit www.arcitura.com/ccp.
The architectural model upon which this design pattern is based is further covered in:
Cloud Computing Design Patterns by Thomas Erl, Robert Cope, Amin Naserpour
(ISBN: 9780133858563, Hardcover, ~ 528 pages)
For more information about this book, visit www.arcitura.com/books.


